Fig. 3.
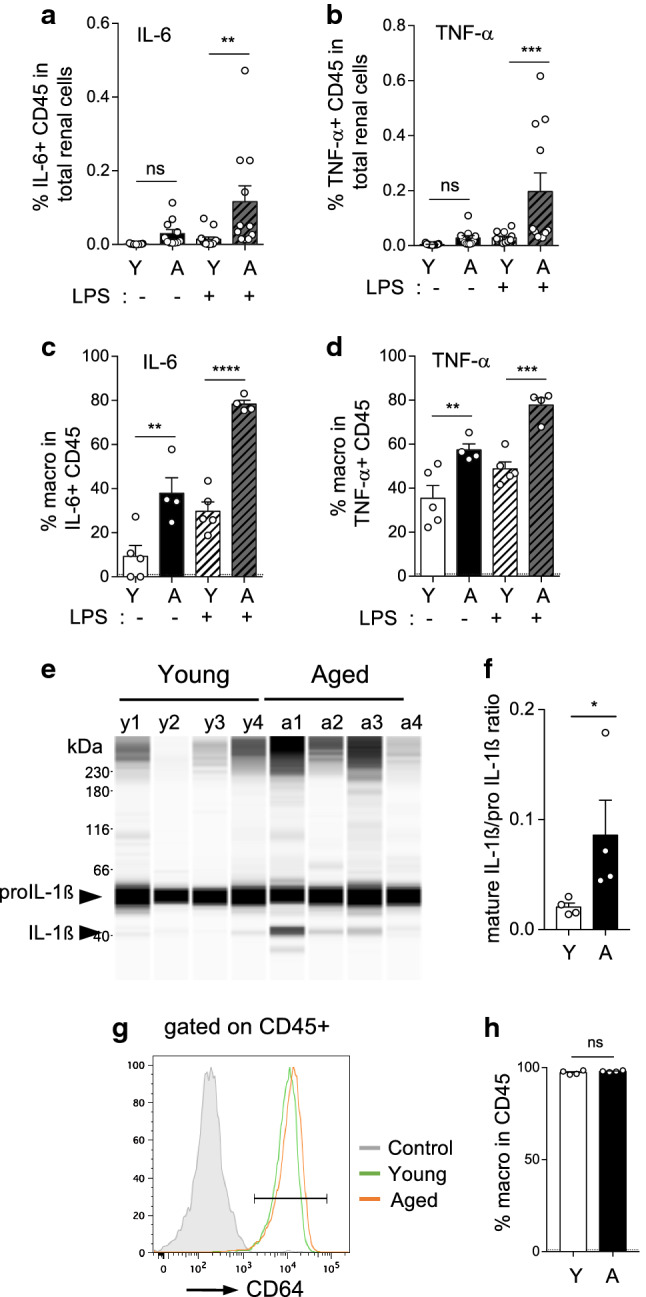
Immune cells are the principal source of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the aging kidney. a–d Percentage of immune cells (CD45+) positive for IL-6 (a) or TNF-α (b) in total renal cells of young (n = 13) or aged (n = 11) mice, with or without LPS stimulation for 4 h, determined by flow cytometry after intracellular staining. Percentage of macrophages (CD64+ MHCII+ CD45+) in IL-6+ CD45+ (c) or in TNF-α+ CD45+ (d) are shown (young, n = 5; aged n = 4). e, f Capillary western blot image (e) and ratio quantification (f) of mature IL-1ß and pro-IL-1ß in protein extracts of CD45+ immune cells, cell sorted by flow cytometry from primary cell cultures of young and aged kidneys at day 7 (n = 4 mice per group). g, h Flow cytometry analysis of primary cell cultures of young or aged kidneys (n = 4 per group) showing the percentage of macrophages (CD64+) in CD45+ immune cells at day 7. Significant differences were evaluated by Two-way RM ANOVA with Sidak’s post hoc test (a–d) **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, *P < 0.05, ns, not significant, or with Mann–Whitney t test (f, h). a Interaction P = 0.0261; Age *P < 0.05; LPS **P < 0.01, b Interaction P = 0.0163; Age **P < 0.01; LPS **P < 0.01, c Interaction P = 0.0085; Age ***P < 0.001; LPS ****P < 0.0001, d Interaction ns; Age **P < 0.01; LPS **P < 0.01
