Extended Data Fig. 1. Identifying human-chimpanzee expression changes using hybrid cells.
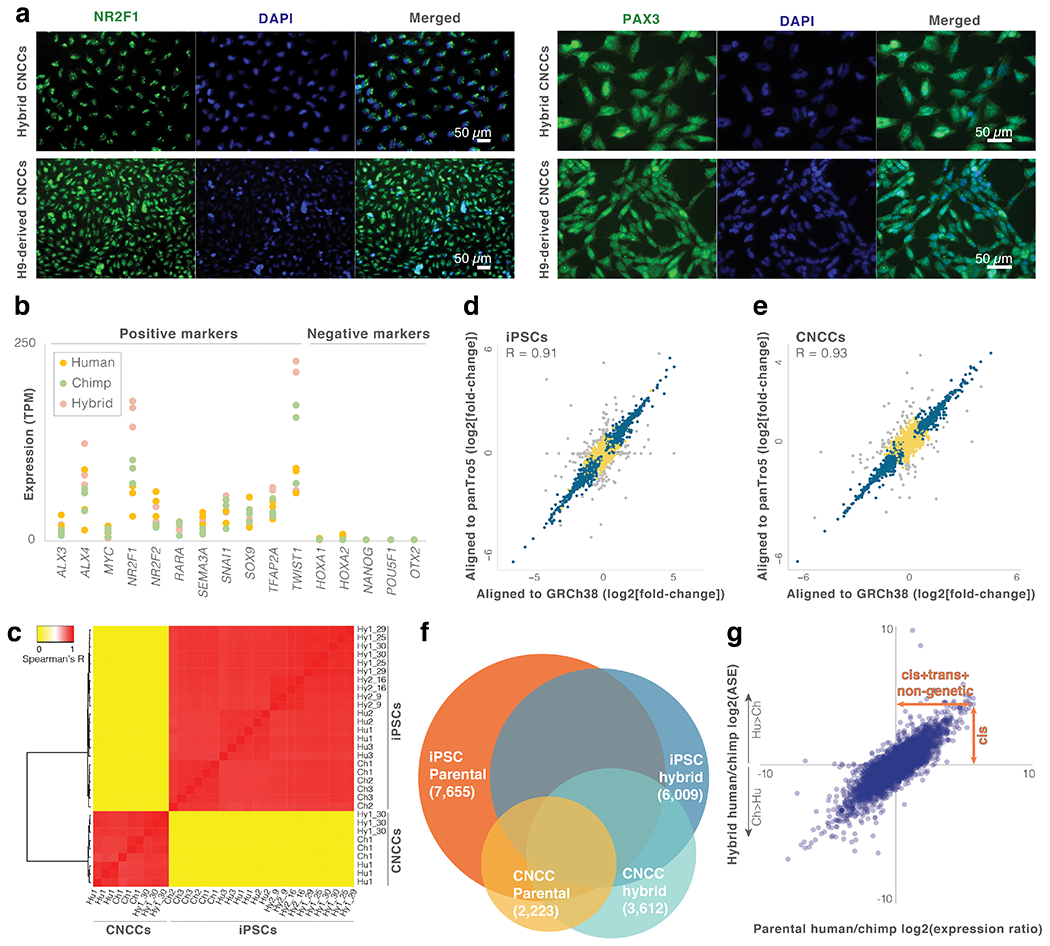
a. Immunostaining for CNCC markers NR2F1 and PAX3 was performed to confirm CNCC differentiation. b. Expression levels of positive and negative markers in the parental and hybrid CNCCs. c. Heatmap and dendrogram of total gene expression across iPSC and CNCC samples. d,e. Fold-change per gene for hybrid iPSCs and hybrid CNCCs when aligned to the human (GRCh38) vs chimpanzee (panTro5) genomes. Grey points are genes where the absolute difference in log2(fold-change) when aligned to the human vs. chimpanzee genome is greater than 1 (i.e., genes with potential alignment bias that were excluded from the analysis). Genes with no observable alignment bias are marked with blue (significant ASE: q-value < 0.05) or yellow (non-significant ASE). f. Venn diagram of genes with significant human-chimpanzee expression changes in parental and hybrid samples. g. Parental vs hybrid iPSC expression changes. See Fig. 1d legend.
