Fig. 1. Study overview.
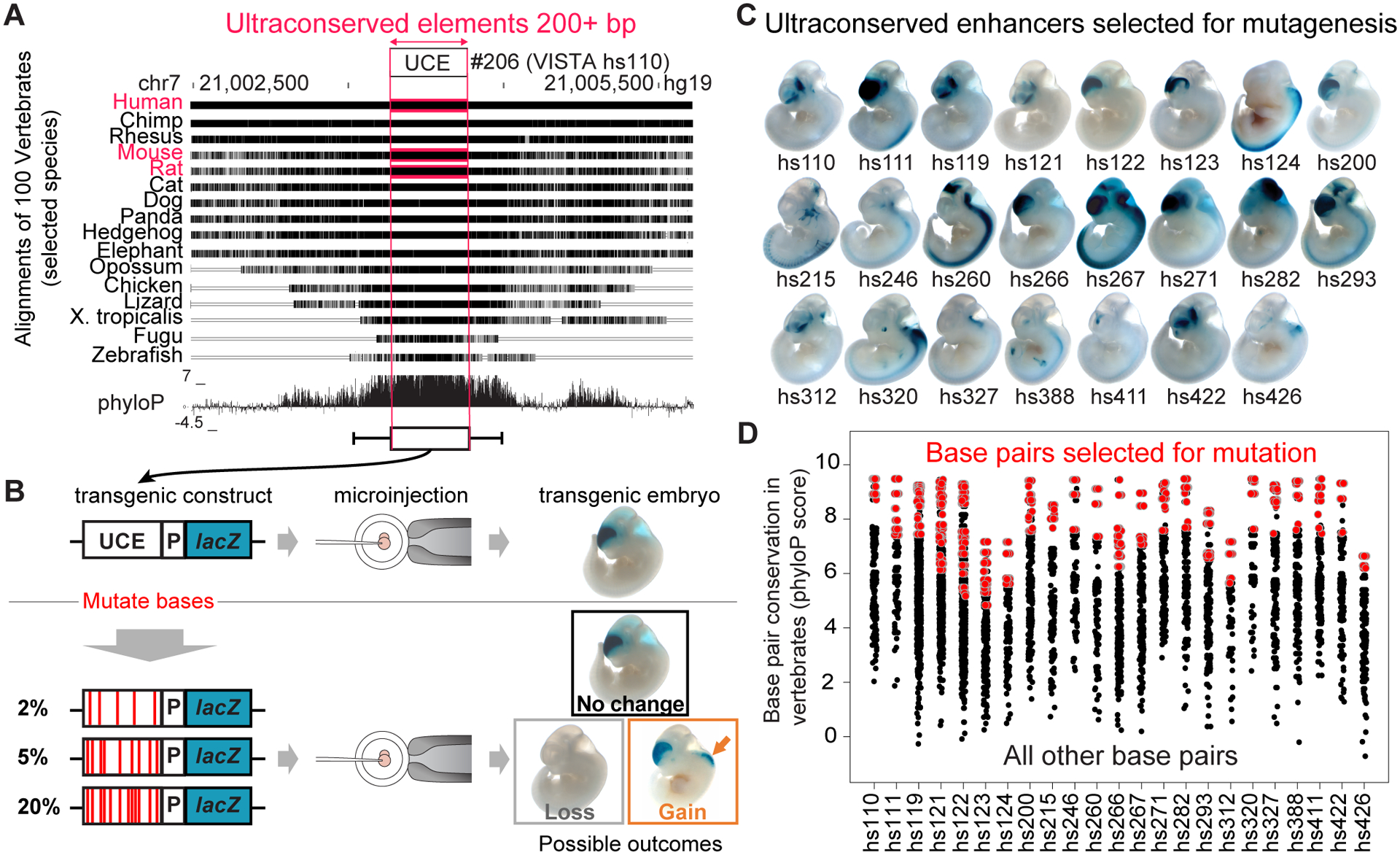
a, Human-rodent ultraconserved elements show a high degree of conservation across other sequenced vertebrate genomes. UCE, ultraconserved element. b, Study design for mouse transgenic reporter assays to reveal whether mutations in ultraconserved enhancers impact their activity. P, promoter. c, Activity of the human reference allele of 23 ultraconserved enhancers selected for mutagenesis. All elements were tested with a CRISPR-assisted site-specific mouse transgenic reporter assay at mouse embryonic day 11.5 (e11.5) except hs124, which was tested at e12.5. d, Conservation of all human-rodent ultraconserved base pairs within the selected 23 ultraconserved enhancers across 100 sequenced vertebrate genomes (phyloP score obtained from UCSC phyloP100way track). Base pairs selected for mutagenesis are highlighted in red. More details on selecting base pairs for mutagenesis can be found in Extended Data Figure 1a and Supplementary Figure 2.
