Figure 6.
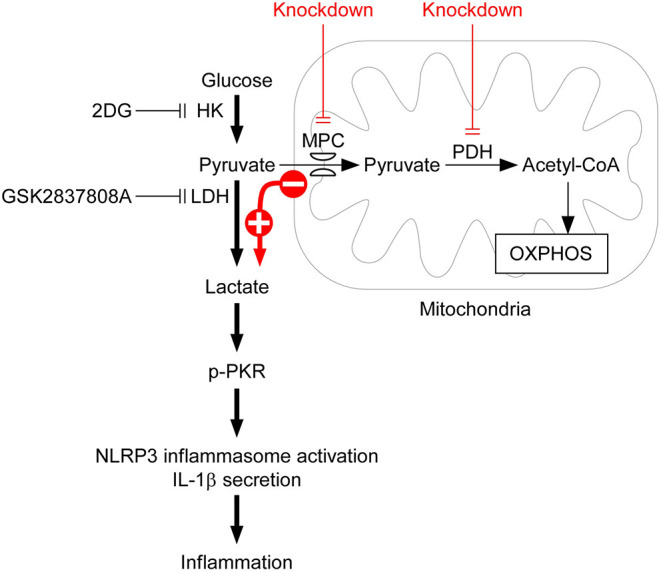
Model for lactic acid fermentation-dependent activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Upon stimulation with NLRP3 inflammasome agonist, HK-dependent glycolysis is activated and contributes to NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Based on the results obtained in this study, we propose that lactic acid fermentation following glycolytic flux is required for NLRP3 inflammasome activation, whereas pyruvate oxidation is not. By contrast, downregulation of lactic acid fermentation by 2DG or GSK2837808A inhibits lactate-dependent phosphorylation of PKR and consequently prevents NLRP3 inflammasome activation, IL-1β secretion, and inflammation. Although pyruvate oxidation converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, which is important for fueling respiration, inhibition of pyruvate oxidation by depletion of either MPC or PDH reprograms pyruvate metabolism from mitochondrial pyruvate-driven respiration to cytoplasmic lactic acid fermentation, and subsequently enhances activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome.
