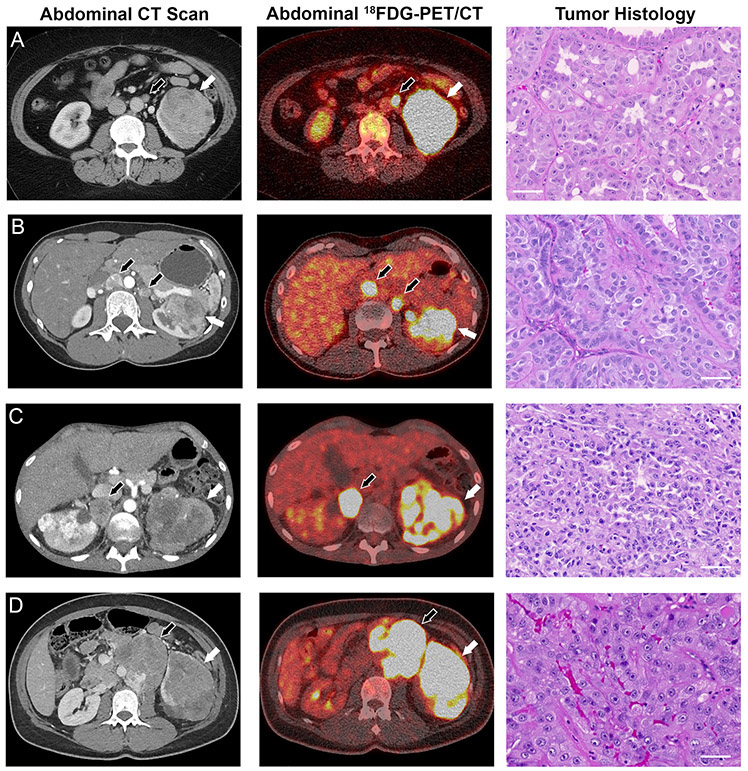
Figure 1: Manifestations of FH−/− renal cell carcinoma in four HLRCC patients.
(A) A contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan revealed a 7 cm mass on the left kidney of patient 3. 18FDG-PET imaging demonstrated both intra- and extra-renal avidity indicative of locally advanced disease and lymph node metastasis, and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of tumor tissue revealed high grade type 2 papillary renal cell carcinoma. (B) A CT scan of patient 4 revealed a 6 cm left kidney tumor and enlarged retroperitoneal lymph nodes. 18FDG-PET suggested regional lymph node involvement as well, and H&E staining revealed high grade type 2 papillary renal cell carcinoma. (C) Patient 5 showed evidence of bilateral kidney lesions and retroperitoneal lymph node metastases. The kidney lesions and metastases showed avidity on 18FDG-PET imaging, and H&E staining of the tumor post mortem revealed high grade type 2 papillary renal cell carcinoma. (D) Patient 6 exhibited a mixed solid/cystic left kidney lesion with hilar adenopathy. 18FDG-PET imaging revealed PET-positive renal mass and extra-renal retroperitoneal metastases, and H&E staining revealed that the lung metastases from patient 6 were high grade type 2 papillary renal cell carcinoma. White arrows indicate primary tumors, black arrows indicate metastases. Scale bars = 50μm.