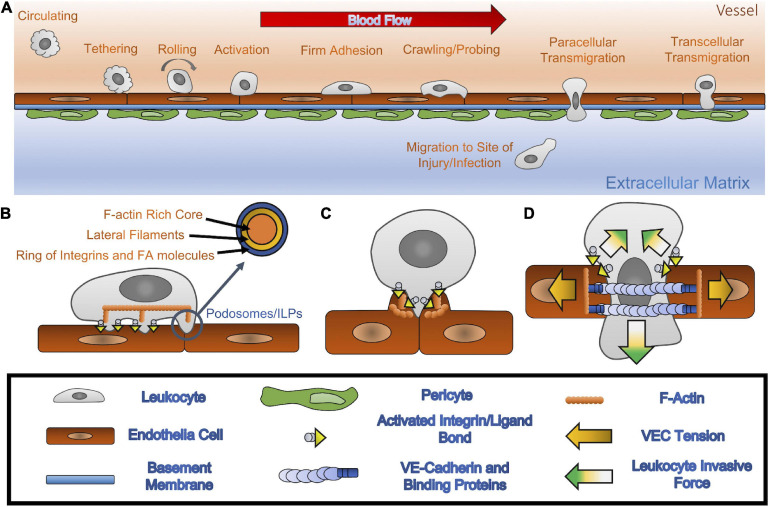
FIGURE 1.
(A) Leukocyte extravasation: through the presence of inflamed VECs, circulating leukocytes localize themselves in the proximity of affected tissues. Once in range, leukocytes use carbohydrate ligands to tether themselves to VECs that express specific selectins. Once tethered, the leukocyte is then able to roll along the endothelium by creating and breaking bonds between the selectins and carbohydrate ligands. Upon the activation of integrins into a high affinity state, triggered by chemokines binding to leukocyte’s chemokine receptors, the leukocyte can transition into a firm adhesion state that stops the rolling and allows the leukocyte to spread out. The leukocyte then crawls and probes the vessel wall in search of VEC hotspots through which it is then able to transmigrate. This maneuver allows for leukocytes to breach the endothelium and basement membrane, thus permitting them to reach the affected tissue area. (B) Crawling/probing: leukocyte-VEC interactions, through high affinity integrins coupled with their respective CAMs, allow the leukocyte to migrate laterally, with the CAMs dictating the migration pattern of the leukocyte along the vascular wall. Furthermore, the leukocyte can convert focal adhesions to invadosome/podosomes like protrusive (ILP) structures, which are sensory organelles that they then utilize to search for TEM hotspots. (C) The transmigratory docking structure: once a hotspot is identified, a cluster of ICAM-1 creates a cup formation to hold on to the transmigrating leukocyte. This docking structure allows the leukocyte to transition from lateral migration to TEM. (D) TEM (paracellular): once in position at the sides of the VEC junction, leukocytes can increase VEC contractility, disrupting the local monolayer tension and creating strong downward pushing forces, which allow for a junctional gap to form and increase in size, and for invasion of the basement membrane. This widened gap allows for the leucocyte to push through the junction and break cellular bonds between VECs.