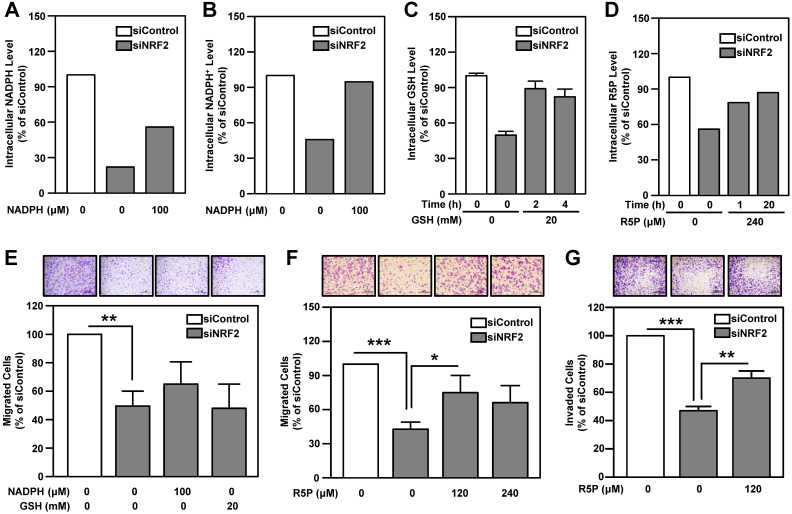
Figure 7.
The role of PPP-related metabolites in rescuing cell motility and invasiveness of NRF2-knockdown HNSCC cells. Effects of NADPH supply on intracellular NADPH (A) and NADP+ (B) levels in NRF2-knockdown Ca9-22-D1 cells. Intracellular NADPH and NADP+ levels were measured after incubation with or without 100 μM NADPH for 4 h. (C) Effects of GSH supply on intracellular GSH levels in NRF2-knockdown Ca9-22-D1 cells. Intracellular GSH was measured after incubation with or without 20 mM GSH for 2 h or 4 h. (D) Effects of R5P supply on intracellular R5P in NRF2-knockdown Ca9-22-D1 cells. Intracellular R5P was measured after incubation with or without 240 μM R5P for 1 h or 20 h. Intracellular metabolite levels were normalized to those of the respective siControl without treatment. (E) The effects of NADPH and GSH on cell migration ability in NRF2-knockdown Ca9-22-D1 cells. Cell motility (F) and invasiveness (G) were determined by trans-well migration or invasion assay in NRF2-knockdown Ca9-22-D1 cells in the presence or absence of R5P. The data are expressed as the mean ± S.D. from three individual experiments. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.