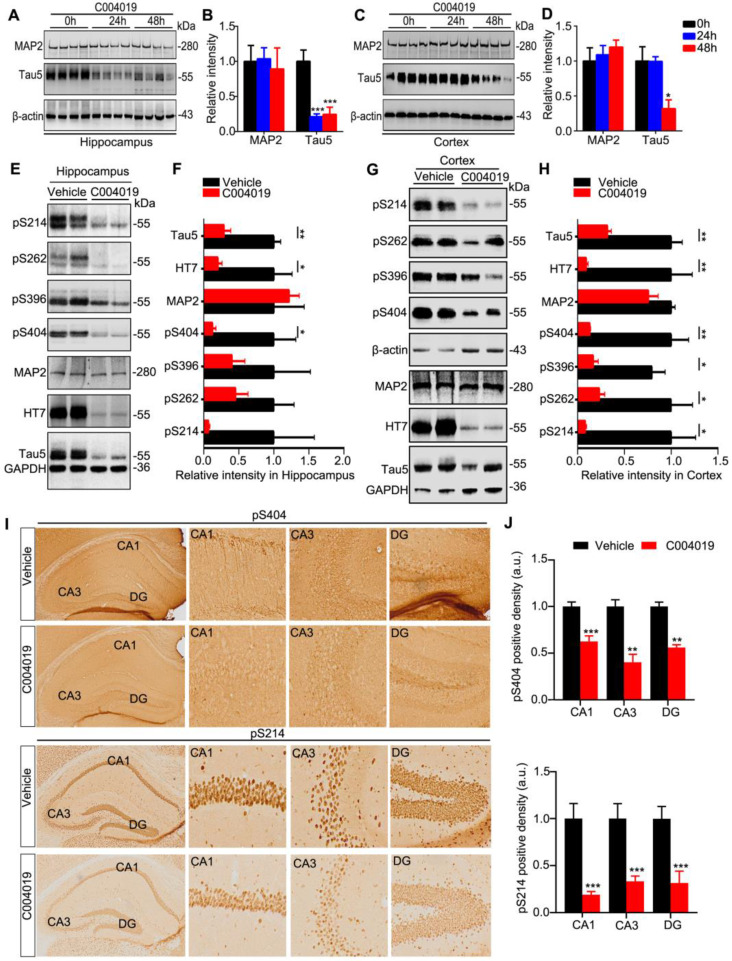
Figure 2.
Intracerebroventricular infusion of C004019 decreased tau in 4 m-old wild-type mice and 9.5 m-old 3xTg AD mice. (A-D) Single-dose intracerebroventricular infusion of C004019 (5 µL, 200 µM) for 24 h and 48 h decreased tau level without affecting MAP2 in hippocampus (A-B) and cortex (C-D) in wild-type mice, more significantly in the hippocampus. β-actin was used as a loading control. (E-H) Intracerebroventricular infusion of C004019 (5 µL, 200 µM) in 9.5 m-old 3xTg-AD mice for 48 h significantly decreased total tau and the tau phosphorylated at multiple-doses AD-related sites in hippocampus (E-F) and cortex (G-H) measured by Western blotting. (I-J) C004019 decreased pS214 and pS404 tau in hippocampal CA1 and CA3 subsets measured by immunohistochemistry (Scale bar: 50 µm). GAPDH with same exposure in the same membrance was used as a loading control. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM, (B, D) *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 vs. 0 h. (F, H, J) *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001vs. Vehicle. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA.