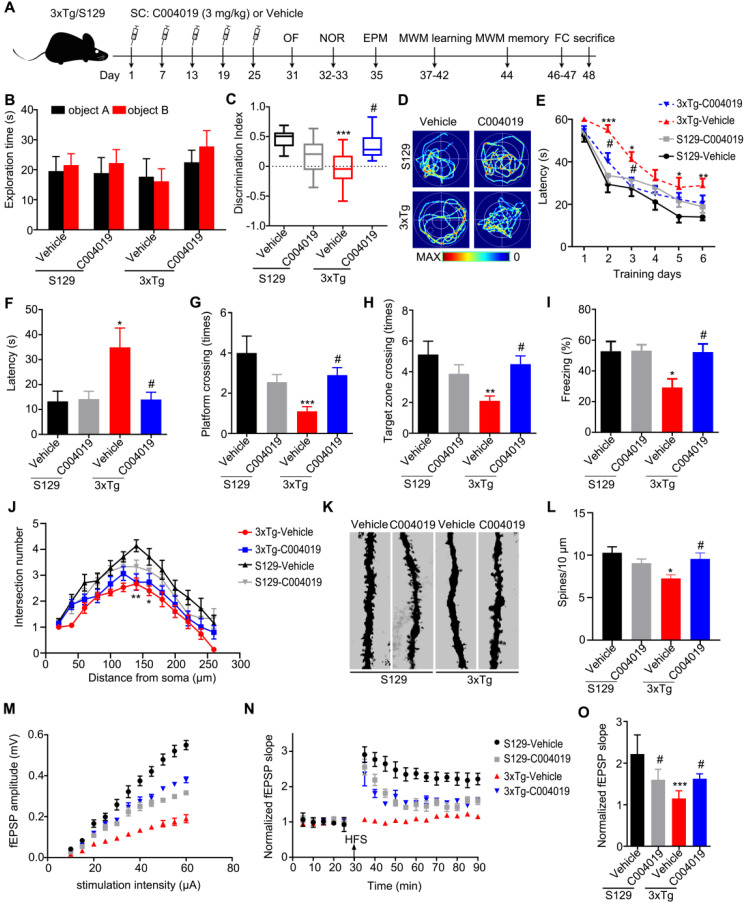
Figure 6.
Multiple-doses subcutaneous administration of C004019 attenuated the cognitive and synaptic deficits in 3xTg-AD mice. (A) Treatment procedure: C004019 (3 mg/kg) or the vehicle was injected subcutaneously every 6 days for one month in 9.5 m-old 3xTg-AD or S129 mice, and then the cognitive behaviors were detected. (B-C) C004019 treatment increased the discrimination index in 3xTg mice measured by NOR. (D-H) In MWM test, C004019 decreased the latency to find platform during learning trial and increased the latency, platform crossings and target zone crossings during the probe trial. (I) C004019 increased the freezing index in 3xTg mice during FCT. (J) C004019 didn't affect neurite arborization measured by Sholl analysis. (K-L) C004019 increased spine density measured by Golgi-cox staining (at least 20 neurons from 3 ∼ 4 mice for each group were analysed for spine density). (M-O) C004019 rescued synaptic functions as shown by an increased input-output response with potentiation of LTP indicated by an increased slope of the evoked fEPSP; the increase was still significant at 60 min after high frequency stimulation (HFS) (n = 8 hippocampal slices from 3 ~ 4 mice in each group). Data were expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 9 ∼ 10 for each group), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. S129-Vehicle. #P < 0.05 vs. 3xTg-Vehicle. Data in (B, C, F-I, L, O) were analyzed by one-way ANOVA. Data in (E, J) was analyzed by two-way repeated-measures ANOVA.