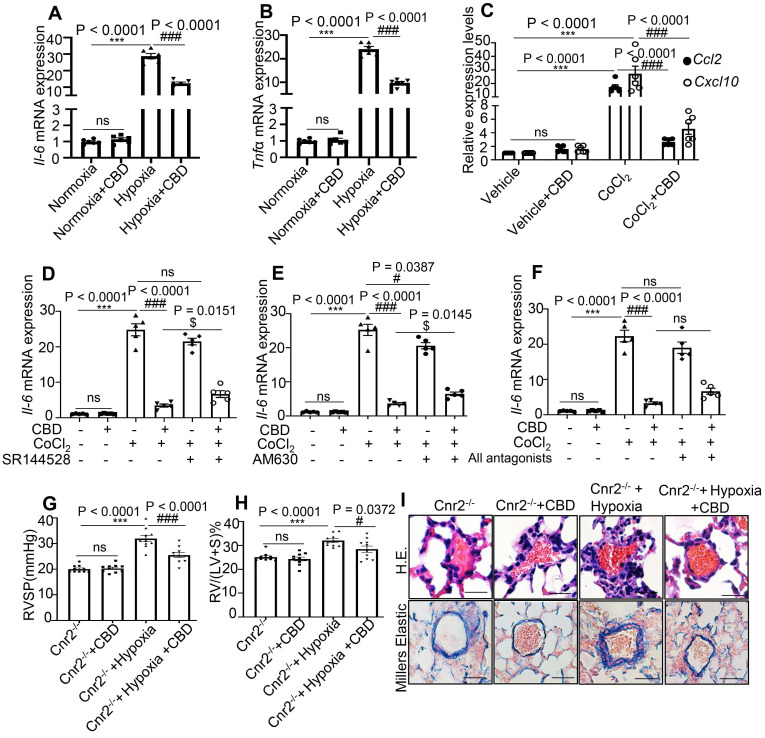
Figure 3.
CBD inhibited inflammation in PAH without canonical cannabinoid receptors involvement. A-B, mRNA levels of Il6 and Tnfα assessed in the lungs of hypoxia-induced preventive PAH mouse model. C, mRNA levels of Ccl2 and Cxcl10 assessed in the mice PASMCs with or without CoCl2 treatment. D-F, mRNA level of Il6 in mice PASMCs treated with CoCl2, and the effect of antagonists of cannabinoid receptors (SR144528, AM630 and both), the concentration of the antagonists was 10 µM, which was equal to the concentration of CBD, the antagonists were pre-treated for 30 min before CBD added, n = 6 per group. G-H, Assessments of RVSP, RVH in the PAH Cnr2-/- mice, n = 10 per group. I, Representative images of pulmonary arteries stained with H&E and elastin of Cnr2-/- and WT littermate controls with or without Sugen hypoxia-induced or daily CBD-treated, scale bar = 20 µm. The results were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's multiple comparison test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. the control group, and #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. the hypoxia or CoCl2 treatment group, $P < 0.05 vs. the CoCl2 with CBD group.