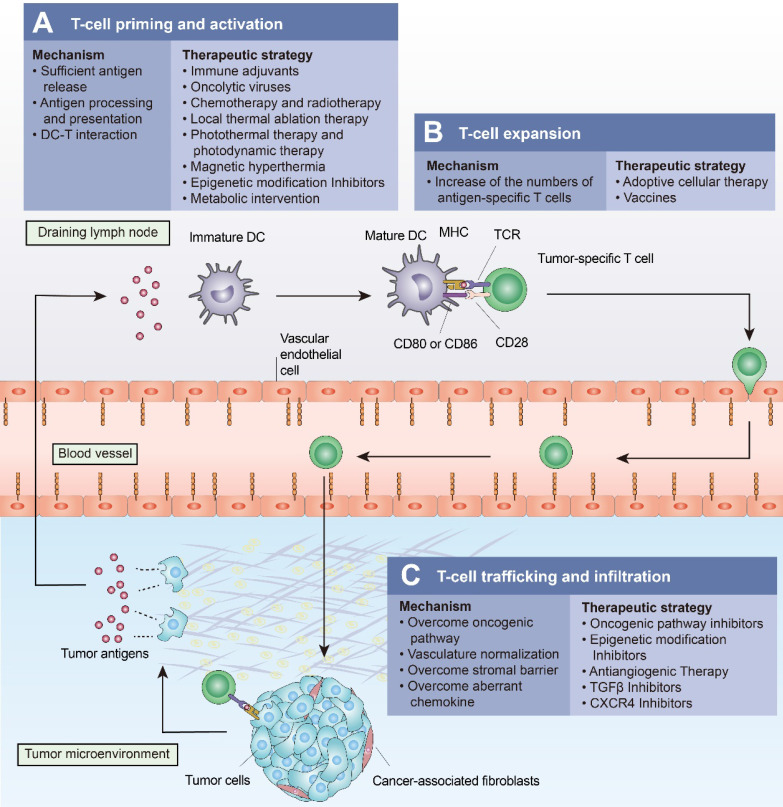
Figure 4.
Approaches to turn a “cold tumor” into a “hot tumor”. Some representative approaches that lead to increased T-cell infiltration and improved efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors are highlighted here. (A) Oncolytic viruses, local thermal ablation therapy (e.g., radiofrequency ablation), chemotherapy, and radiotherapy are all capable of inducing immunogenic cell death (ICD) to promote T-cell priming and activation. Local administration of immune adjuvants such as TLR agonists promotes the activation of dendritic cells (DCs). Epigenetic modification inhibitors can promote T-cell priming by increasing the expression of tumor antigens and by restoring antigen processing and presentation mechanisms. (B) Cancer vaccines and adoptive cellular therapies, such as CAR-T cells, can promote the expansion of tumor-specific T lymphocytes. (C) Intrinsic oncogenic pathway inhibitors, epigenetic modification inhibitors, antiangiogenic therapies, TGFβ inhibitors, and CXCR4 inhibitors promote T-cell trafficking and enable T cells to infiltrate the tumor more effectively.