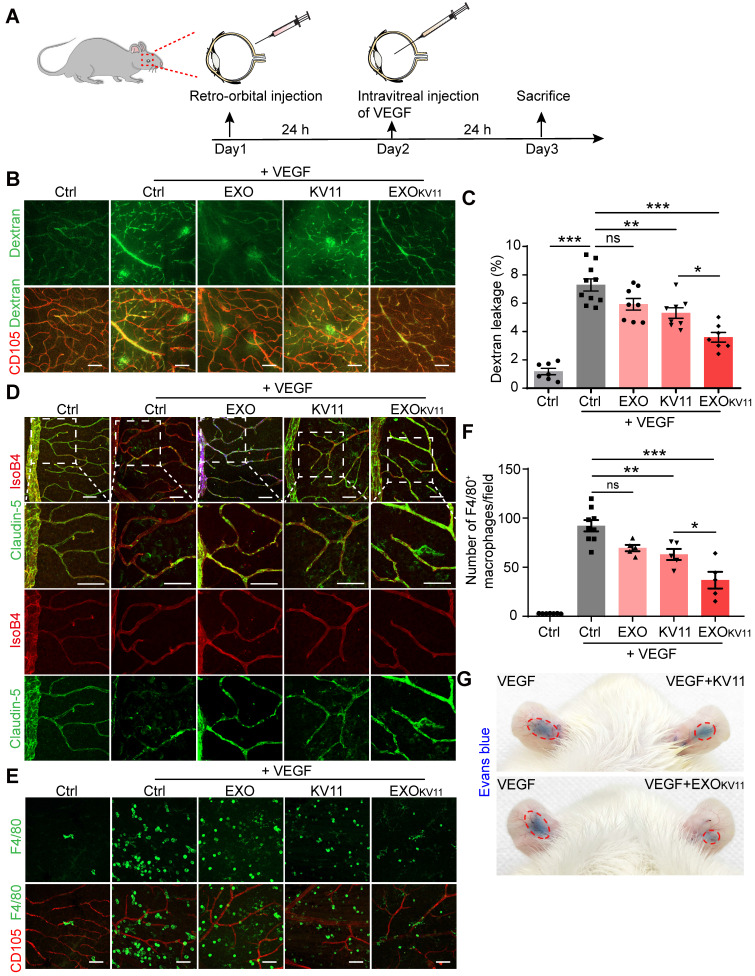
Figure 5.
EXOKV11 suppresses VEGF-induced vascular leakage in vivo. (A) Schematic depiction of the pre-treatment procedure in a VEGF-induced vascular leakage model. EXOKV11, KV11, EXO, or vehicle was retro-orbitally injected in adult wild type C57BL/6J mice. After 24 h, 100 ng VEGF was intravitreally injected to induce vascular leakage in the retina. The mice were sacrificed for analysis after another 24 h. (B) FITC-dextran was injected and the retinas were harvested at the endpoint. Representative images of flat-mounted retina show extravasated FITC-dextran and CD105+ vessels. (C) Quantification of dextran leakage in (B) (n = 7 - 10 mice per condition). (D) Representative confocal images of anti-CD105, anti-Claudin-5-stained retinal vessels in mice treated as in (A). (E) Representative images of F4/80+ macrophages (green) and CD105+ vessels in retinas treated as in (A). (F) Quantification of macrophage infiltration in (E) (n = 4 - 9 mice per condition). (G) Representative photographs of Evans blue leakage in SD rats ears in an auricular Miles assay with intradermal injection with VEGF, VEGF+KV11 mixture, or VEGF+EXOKV11 mixture. The data represent as mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparisons test in (C), (F). Scale bars, 50 µm.