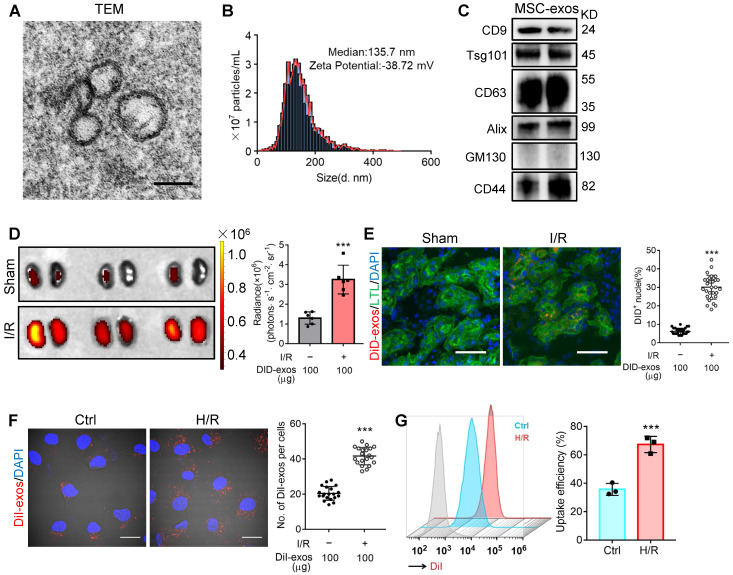
Figure 1.
MSC-exos homing to injured kidney. (A) Morphology of MSC-exos under TEM. Scale bars, 100 nm. (B) Representative nanoparticle tracking analysis of MSC-exos. (C) Western blotting analysis of exosomal-associated (CD9, CD63, Tsg101, and Alix), Golgi-associated (GM130), and MSC-associated (CD44) markers in MSC-exos. (D) Imaging of fluorescence intensity in sham and I/R kidneys (n = 6). (E) Fluorescent images showed the accumulation of DiD-labeled MSC-exos in renal tubules of I/R mice. Scale bars, 25 μm. (F) Representative fluorescent images showed the uptake of DiI-labeled MSC-exos by H/R-treated HK-2 cells. Scale bars, 10 μm. (G) DiI-positive HK-2 cells were detected by flow cytometry. The blue peak represented the control and the red one represented H/R-treated HK-2 cells internalizing DiI-labeled MSC-exos. Data are presented as mean ± SD, ***p < 0.001, unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test.