Fig. 5.
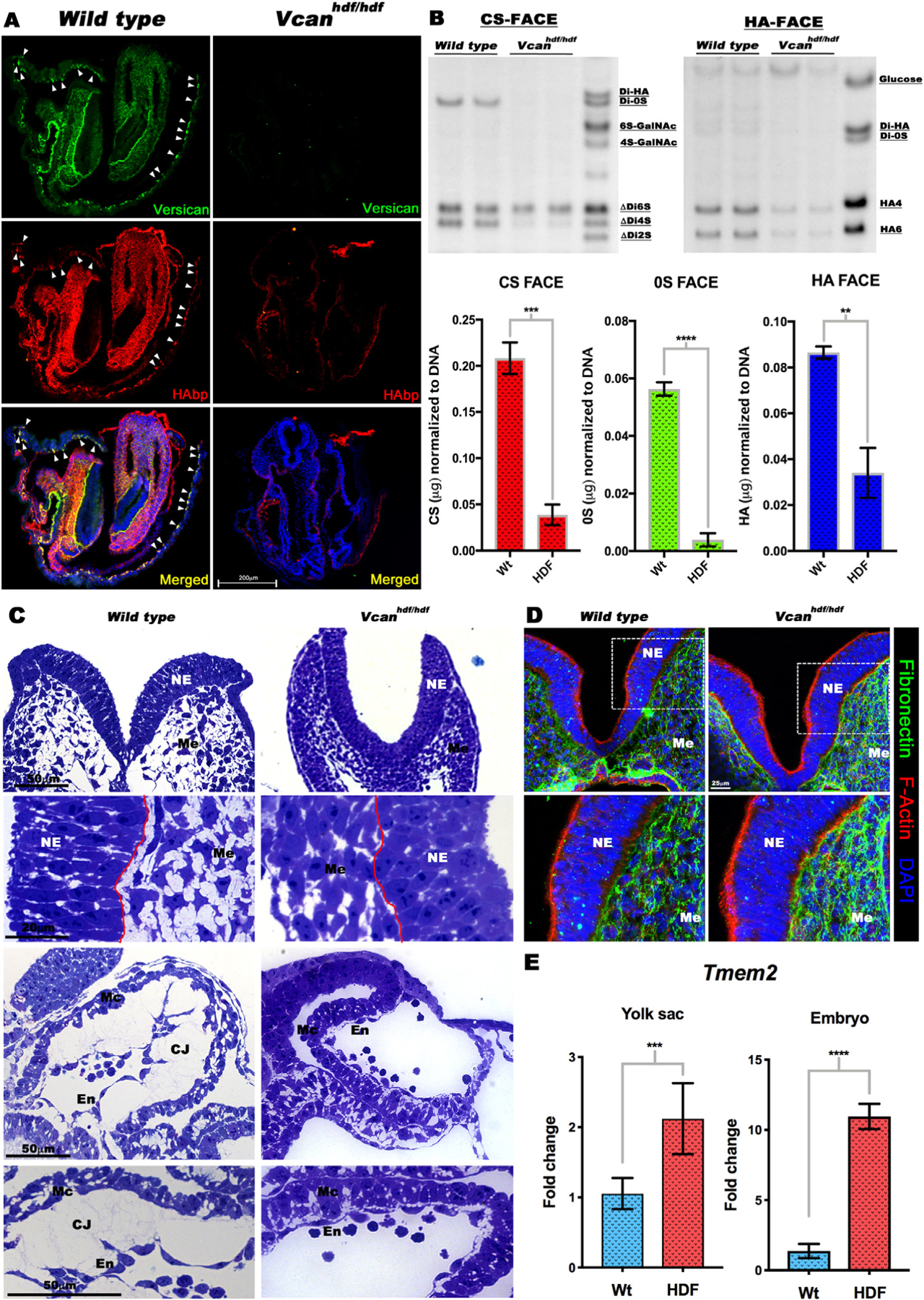
Vcan inactivation results in loss of hyaluronan. (A) Versican (green) and HAbp (red) staining of E8.5 wild type and Vcanhdf/hdf embryos showing severely reduced HAbp staining in Vcanhdf/hdf embryos. Arrowheads indicate versican and HAbp-stained yolk sac blood islands (n=3 embryos each genotype). (B) (Top) Fluorophore-assisted carbohydrate electrophoresis (FACE) analysis for chondroitin sulfate (CS-FACE) and hyaluronan (HA-FACE) in E8.5 littermate embryos. Versican is the major CS-proteoglycan in E8.5 embryos. HA content is significantly reduced in Vcanhdf/hdf embryos. (Bottom) Quantification of CS and HA FACE, normalized to DNA (n=4 embryos from each genotype, error bars= S.E.M.,**, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; ****, p<0.0001). (C) 1 μm thick, toluidine blue-stained Eponate 12 sections from E8.5 wild type and Vcanhdf/hdf embryos showing compaction of craniofacial mesenchymal cells (Me) and loss of cardiac jelly (CJ) between the myocardium (Mc) and endocardium (En). The red line indicates the boundary of neural epithelium (NE) with mesenchyme (n=3 embryos each genotype). (D) E8.5 wild Vcanhdf/hdf embryo sections stained with F-actin (red) and fibronectin (green) showing stronger fibronectin staining (n=3 embryos each genotype). (E) RT-qPCR shows increased Tmem2 mRNA in Vcanhdf/hdf embryos and yolk sacs (n=3 embryos and yolk sacs from each genotype, error bars= S.E.M., ***, p<0.001; ****, p<0.0001). Scale bar in A= 200μm, 50μm, 20μm in C D=25 μm.
