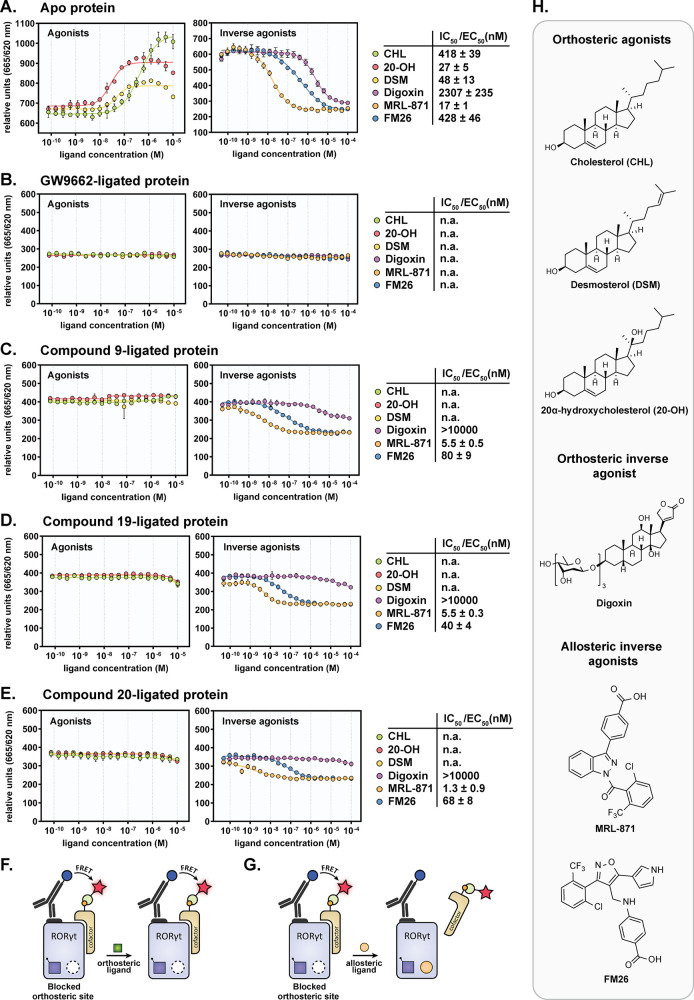
Figure 3.
TR-FRET coactivator recruitment ligand binding assay with RORγt (unligated and ligated) by titration of various orthosteric and allosteric ligands. (A) Apo (unligated) RORγt protein. (B) GW9662-ligated RORγt. (C) Compound 9-ligated RORγt. (D) Compound 19-ligated RORγt. (E). Compound 20-ligated RORγt. Data recorded in triplicate from two independent experiments (one representative data set shown). Error bars represent the SD of the mean. Abbreviations: n.a., not active. (F/G) Schematic representation of the TR-FRET coactivator recruitment assay, using the ligated protein. (F) Orthosteric ligand binding will be occluded, showing no effect on the initial coactivator recruitment capacity. (G) Allosteric ligand binding will result in reduced coactivator binding and therefore a lower FRET pairing. (H) Chemical structures of orthosteric agonists (cholesterol (CHL), desmosterol (DSM), and 20α-hydroxycholesterol (20-OH)), orthosteric inverse agonist digoxin, and allosteric inverse agonists MRL-871 and FM26.