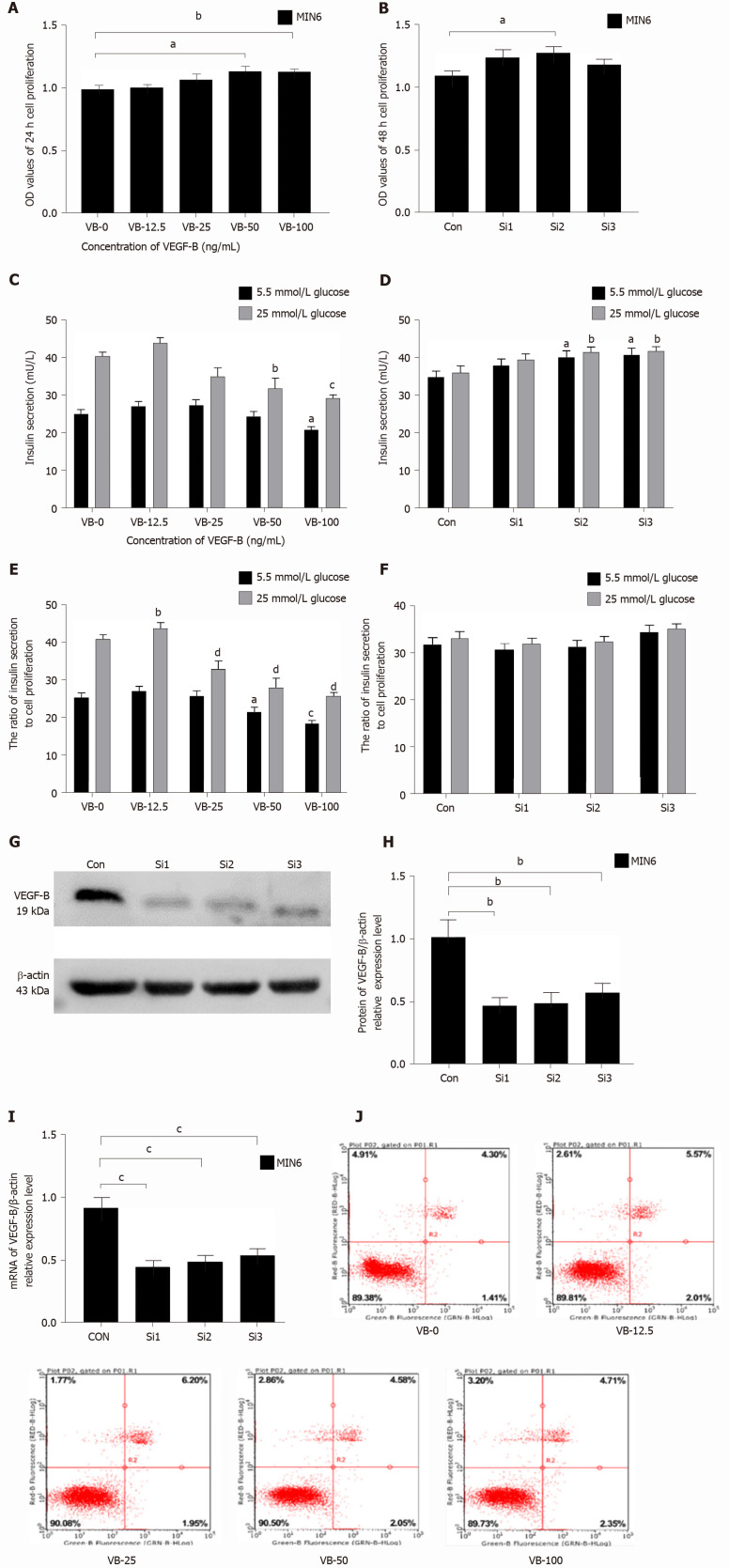
Figure 1.
Decreased insulin secretion in MIN6 cells is related to vascular endothelial growth factor B function. A: Treatment with a gradient concentration of vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGF-B, VB) protein promotes MIN6 cell proliferation. aP < 0.05 vs VB-0, bP < 0.01 vs VB-0; B: MIN6 cells with VEGF-B knockdown show an increasing trend in proliferation. aP < 0.05 vs Control; C: Stimulation with a gradient concentration of VEGF-B protein inhibits insulin secretion by MIN6 cells. aP < 0.05 vs VB-0 in the presence of 5.5 mmol/L glucose; bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs VB-0 in the presence of 25 mmol/L glucose; D: MIN6 cells with VEGF-B knockdown exhibit increased insulin secretion. aP < 0.05 vs Control in the presence of 5.5 mmol/L glucose; bP < 0.05 Control in the presence of 25 mmol/L glucose; E: The ratio of insulin secretion by MIN6 cells to their corresponding proliferation upon stimulation with a gradient concentration of VEGF-B protein. aP < 0.05, cP < 0.001 vs VB-0 in the presence of 5.5 mmol/L glucose; bP < 0.01, dP < 0.001 vs Control in the presence of 25 mmol/L glucose; F: The ratio of insulin secretion in MIN6 cells to its corresponding cell proliferation after knocking down VEGF-B; G and H: Western blot analysis revealing relative VEGF-B protein expression in cells transfected with VEGF-B siRNA and corresponding statistical data. bP < 0.01 vs Control; I: Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction revealing relative VEGF-B mRNA expression in cells transfected with VEGF-B siRNA and corresponding statistical data. cP < 0.001 vs Control; J: Flow cytometry results indicating that VEGF-B does not affect the apoptosis of MIN6 cells. Student's t-test was performed. VEGF-B: Vascular endothelial growth factor B; VB: VEGF-B; Con: Control; Si: Small interfering RNA; MIN6: MIN6 cell; OD: Optical density.