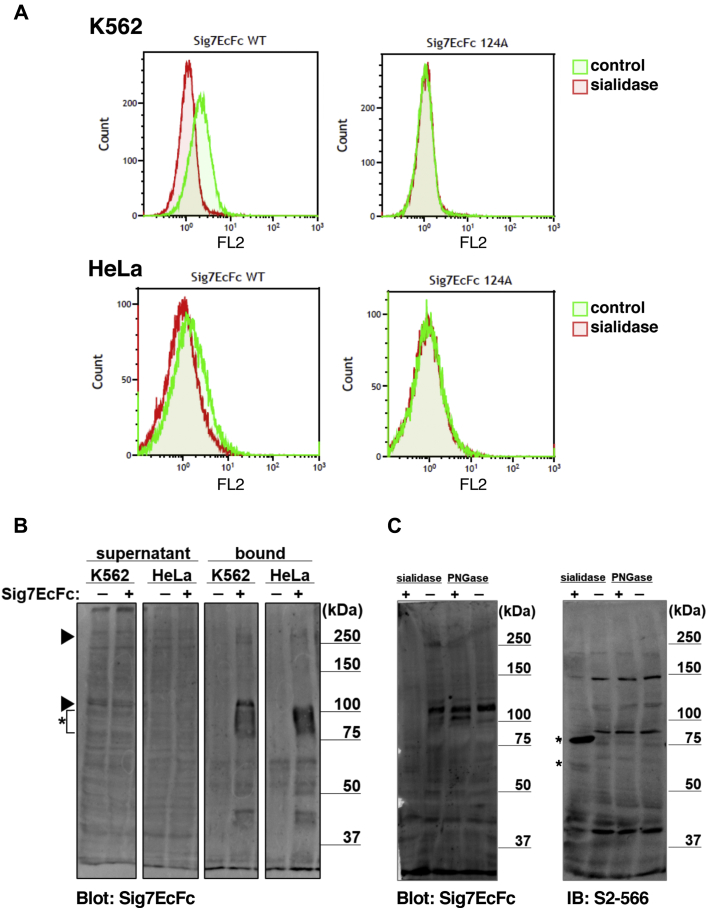
Figure 1.
Binding of Siglec-7 to the ligands in K562 and HeLa cells.A, the binding of Siglec-7EcFc WT (Sig7EcFc WT) and R124A (Sig7EcFc R124A) to the surface of K562 and HeLa cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. Cells treated with sialidase (red) were compared with those untreated (green). B, ligand pull-down of Siglec-7. The K562 or HeLa cell lysate (90 μg) was mixed with (+) or without (−) Siglec-7EcFc (1 μg), and Siglec-7 ligands were pulled down by Protein A-Sepharose (10 μl). Proteins bound to the beads (bound) and supernatant were analyzed by western blotting with Siglec-7EcFc WT (Sig7EcFc). The exogenous Siglec-7EcFc was observed as smear band at 80 to 100 kDa and marked by asterisk. The precipitated 110 kDa and 270 kDa proteins are indicated by arrowheads. C, sialidase and PNGase F treatment for ligands in K562 cells. The K562 cell lysate was treated with (+) or without (−) sialidase (A. ureafaciens sialidase 2.5 mU, V. cholerae sialidase 6.7 mU, pH 5.5) or with (+) or without (−) PNGase (20 U, pH 7.5) and analyzed by western blotting using Siglec-7EcFc WT (Sig7EcFc) or anti-diSiaα2,3-Gal monoclonal antibody (S2-566). The bands derived from sialidases are marked by asterisks.