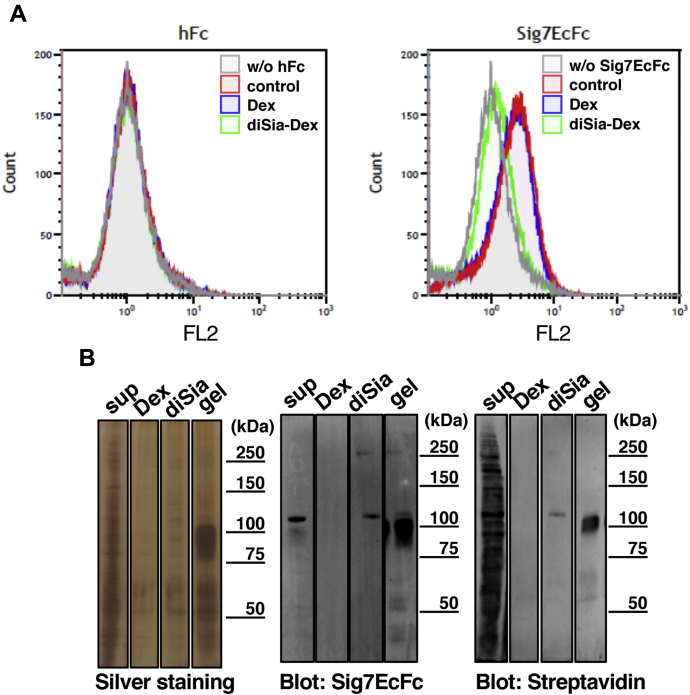
Figure 2.
Effects of diSia-Dex on the binding of Siglec-7 to the ligands of K562 cells.A, the inhibitory effects of diSia-Dex on Siglec-7EcFc binding to K562 cell surfaces were analyzed using flow cytometry. The reaction solution of 10 μg/ml Siglec-7EcFc and anti-hIgG+M+A antibody was mixed with 100 nM Dex or diSia-Dex and subsequently anti-goat IgG-Alexa Fluor 555; then, the fluorescence intensity was measured using flow cytometry. Human Fc was used as a negative control (hFc). Gray: cells incubated without Siglec-7EcFc (w/o Sig7EcFc), red: cells incubated with Siglec-7EcFc without inhibitor (control), blue: cells incubated with Siglec-7EcFc and Dex (Dex), green: cells incubated with Siglec-7EcFc and diSia-Dex (diSia-Dex). B, cell surface biotin labeling and pull-down experiments with Siglec-7. The cell surfaces of K562 were randomly biotin-labeled using Sulfo-NHS-LC-Biotin. Siglec-7 ligands on the cell surface were pulled down from the lysates (400 μg) using Siglec-7EcFc (6 μg) and eluted with 100 nM Dex (Dex) and diSia-Dex (diSia); beads after elution (gel) and the supernatant (sup) were also analyzed. Samples were denatured, and each sample was separated using SDS-PAGE and analyzed using silver staining and western blotting. Ligands were detected using a complex of 0.5 μg/ml Siglec-7EcFc and anti-human IgG+A+M-HRP (Sig7EcFc) or 5000-fold diluted streptavidin-HRP (Streptavidin).