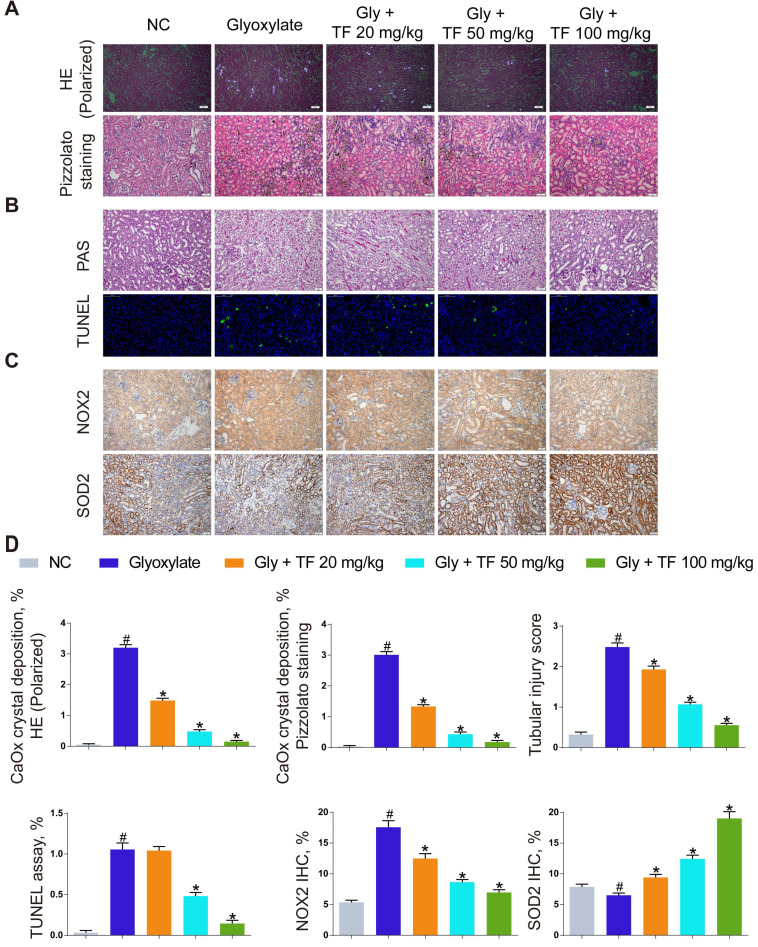
Figure 1.
Theaflavin alleviated CaOx nephrocalcinosis-induced oxidative stress injury and crystal deposition in vivo. (A) CaOx crystal deposition in glyoxylate-induced kidney CaOx nephrocalcinosis mouse model with or without theaflavin treatment was detected by polarized light optical microscope (100× magnification; scale bar: 50 µm) and Pizzolato staining (200× magnification; scale bar: 50 µm). (B) PAS staining illustrating tubular injury (200× magnification; scale bar: 20 µm). TUNEL staining detected renal tubular epithelial cell death (200× magnification; scale bar: 100 µm). (C) IHC staining for NOX2 and SOD2 in CaOx nephrocalcinosis mouse kidney (200×; scale bar: 20 µm). (D) Quantification of CaOx crystal deposition, PAS staining, TUNEL staining, NOX2 and SOD2 IHC staining. n = 6 per group. The data are shown as the mean ± SD. #p < 0.05 vs. the normal control group, *p < 0.05 vs. the glyoxylate group.