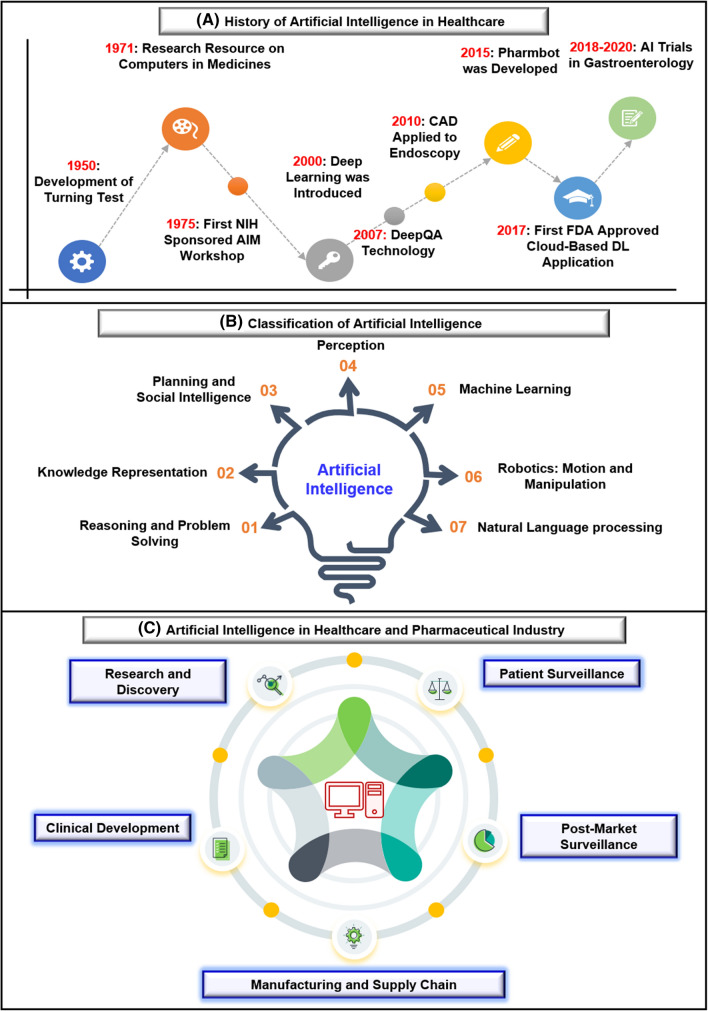
Fig. 1.
a History of artificial intelligence in healthcare: the first breakthrough of artificial intelligence in healthcare comes in 1950 with the development of turning tests. Later on, in 1975, the first research resource on computers in medicines was developed, followed by NIH's first central AIM workshop marked the importance of artificial intelligence in healthcare. With the development of deep learning in the 2000s and the introduction of DeepQA in 2007, the scope of artificial intelligence in healthcare has increased. Further, in 2010 CAD was applied to endoscopy for the first time, whereas, in 2015, the first Pharmbot was developed. In 2017, the first FDA-approved cloud-based DL application was introduced, which also marked the implementation of artificial intelligence in healthcare. From 2018 to 2020 several AI trials in gastroenterology were performed. b Classification of artificial intelligence: there are seven classifications of artificial intelligence, which are reasoning and problem solving, knowledge representation, planning and social intelligence, perception, machine learning, robotics: motion and manipulation, and natural language processing, as discussed by Russel and Norvig in their book “Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach.” Machine learning is further divided into three significant subsets: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and deep learning, whereas vision is divided into two subsets, such as image recognition and machine vision. Similarly, speech is divided into two subsets: speech to text and text to speech, whereas natural language processing is classified into five main subsets, including classification, machine translation, question answering, text generation, and content extraction. c Artificial intelligence in the healthcare and pharmaceutical industry has five significant applications, which change the entire scenario. These applications include research and discovery, clinical development, manufacturing and supply chain, patient surveillance, and post-market surveillance