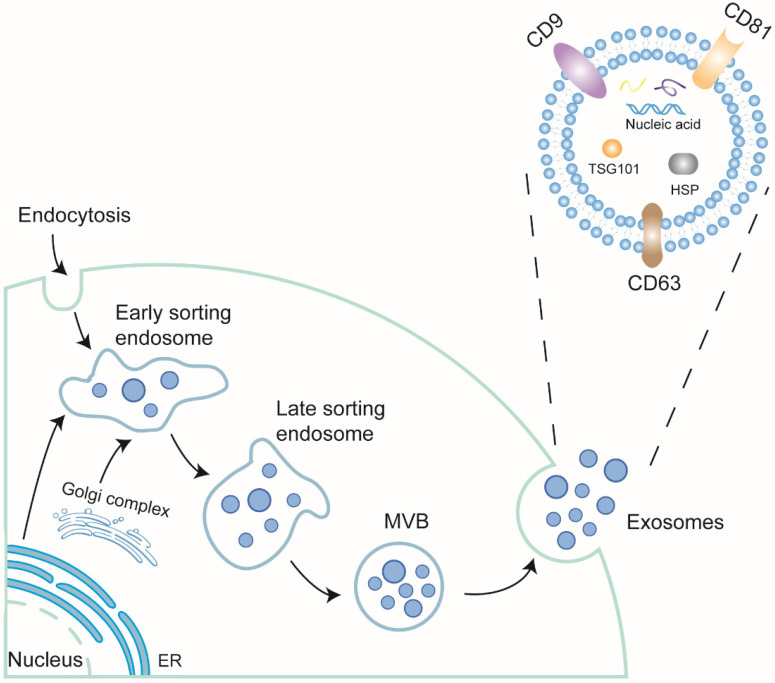
Figure 1.
The biogenesis and structure of exosomes.The plasma membrane firstly invaginates into early sorting endosome (ESE) with the assistance of Golgi complex and endoplasmic reticulum. Then, ESE can generate late sorting endosome (LSE). The LSE undergoes second invagination and forms multivesicular body (MVB). MVB contains a structure called Intraluminal vesicles (ILV), which will be modified further. When MVB fuses with plasma membrane, ILVs will be released. At the time, ILV become exosomes. Exosomes are comprised of lipid bilayer and contents. The contents include nucleic acids (RNAs and DNAs), lipids and proteins. Some proteins are located on the membrane as receptor signals or receptors, some transverse the bilayer, like tetraspanin family, as hallmarks of exosomes, while some are in the exosomes, like TSG101, Alix, also function as hallmarks or play some certain roles.