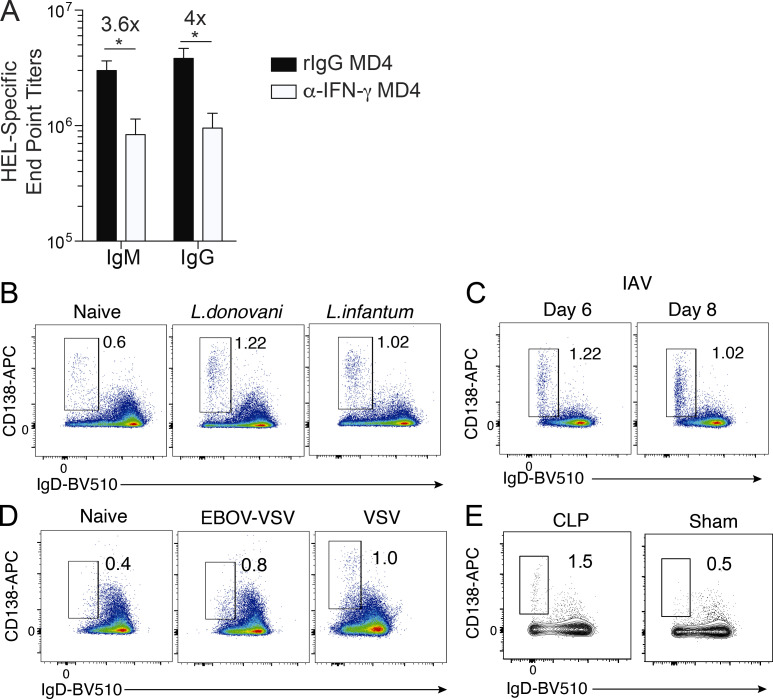
Figure S2.
Serum ELISA data from infected MD4 mice and plasmablast responses in Leishmania, influenza, and VSV-infected mice, and mice subjected to cecal ligation and puncture. (A) MD4 mice were infected with 106 Py pRBCs and administered 500 µg of α-IFN-γ (n = 8; clone XMG1.2) or rIgG (n = 6) on days 0, 3, 6, and 9 p.i. HEL-specific IgM and IgG serum end point titers as measured by ELISA on day 10 p.i. Data are mean ± SEM, representative of four independent experiments, analyzed using unpaired Mann-Whitney tests. (B–E) CD138hiIgDneg splenic plasmablast responses were evaluated on day 10 p.i. in WT mice infected i.v. with 2.5 × 107 of either L. donovani or L. infantum parasites (n = 10 mice/group; B) or intranasally with 100 IU of influenza A virus (IAV; n = 5; C); in IFNAR-deficient mice (n = 6) infected i.p. with 100 PFUs of recombinant VSV (EBOV-VSV; D, middle panel) or WT mice infected with high-dose (1 × 106 PFUs) VSV (D, right panel); or WT mice subjected to cecal ligation and puncture (CLP; n = 4) or sham surgery (n = 4; E). *, P < 0.05.