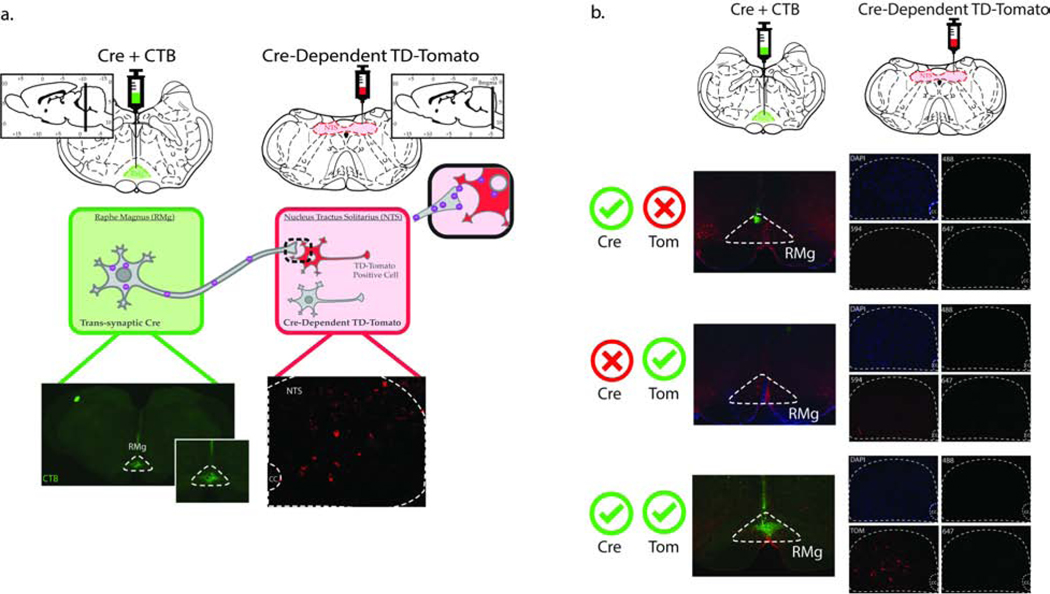
Fig 5. Methods and controls for mono-trans-synaptic viral tracing from the RMg to the NTS.
Rats (n=18) received a cocktail injection containing an AAV1 Cre anterograde tracer and cholera toxin B (CTB)-488 (50nl) into the RMg and a Cre-dependent AAV1-FLEX-TD-Tomato (100nl /hemisphere) virus into the NTS (a). Three weeks following the viral injections the animals were transcardially perfused, brains were harvested, and tissue was processed for FISH/IHC analysis. The site of injection was verified using anti-CTB antibody in the RMg (a, bottom left). The trans-synaptic properties of the AAV1 Cre was confirmed via the presence of TD-Tomato-expressing neurons in the NTS (a, bottom right). Validation for injection site specificity (b, top panels), dependency on the presence of Cre for the expression of TD-Tomato (b, middle panels), and lack of bleed-through of TD-Tomato into other channels (b, bottom panels).