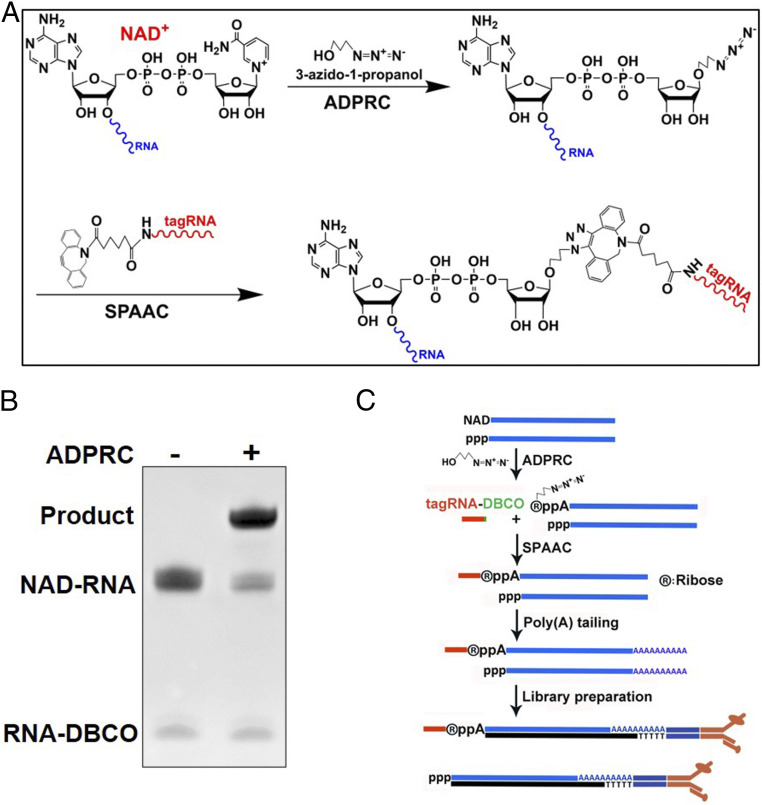
Fig. 1.
The NAD tagSeq II method. (A) Diagram illustrating reactions for labeling NAD-RNAs with a synthetic DBCO-modified RNA tag. In the presence of ADPRC, 3-azido-1-propanol replaces the nicotinamide of NAD-RNA. The azide-functionalized NAD-RNA molecule is then ligated to a synthetic RNA (tagRNA) with a DBCO group at its 3′ end through SPAAC. (B) Tagging of a 38-nt NAD-RNA with the synthetic 16-nt RNA-DBCO. The NAD-RNAs were reacted with 3-azido-1-propanol in the presence of ADPRC (ADPRC+) and then with the 16-nt RNA-DBCO, forming the ligation products. No such ligation product was observed in the reaction without ADPRC (ADPRC−). (C) Workflow of the NAD tagSeq II method for analysis of NAD-RNAs in E. coli. E. coli total RNA samples were subjected to the tagging process as described in A. After depletion of rRNAs from the RNA samples, the RNA samples were subjected to polyadenylation using poly(A) polymerase. The poly(A)-tailed RNA samples were used to make a library for sequencing using Oxford nanopore sequencing. A parallel experiment without ADPRC served as a control.