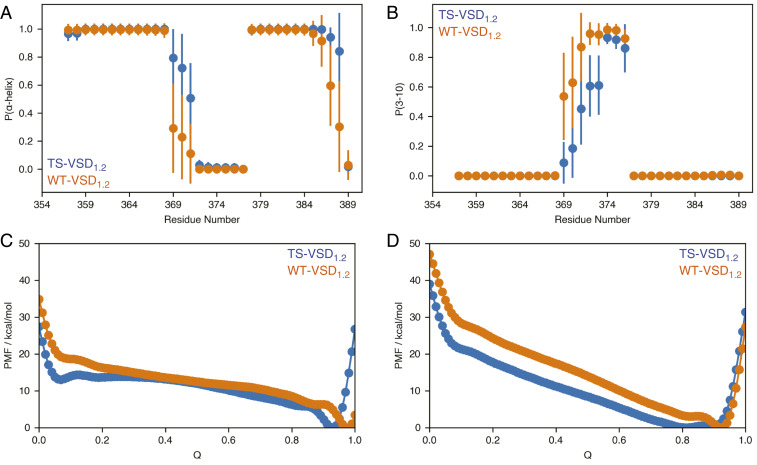
Fig. 4.
MD simulations capture changes in secondary structure propensity and flexibility near the site of mutation in TS-VSD. In conventional MD simulations, the secondary structures around the mutation sites are ordered but show a slight shift in α-helix (A) versus 310-helix (B) propensity in the TS-VSD. The timescale of the MD simulations may not be long enough to fully capture the loss of helical structure observed by NMR. Multiple-walker well-tempered metadynamics simulations reveal that TS-VSD features a higher level of structural plasticity near the mutation sites compared to the WT-VSD, consistent with the NMR data. The potential of mean force (PMF) along the collective variable plotted against the fraction of native contacts (Q) for α-helix (C) and 310-helix (D) from metadynamics simulations reveals an energy minimum at lower fraction of native contacts and lower energy barrier to access low-Q states for the TS-VSD. Convergence behavior of the computed PMFs is shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S10.