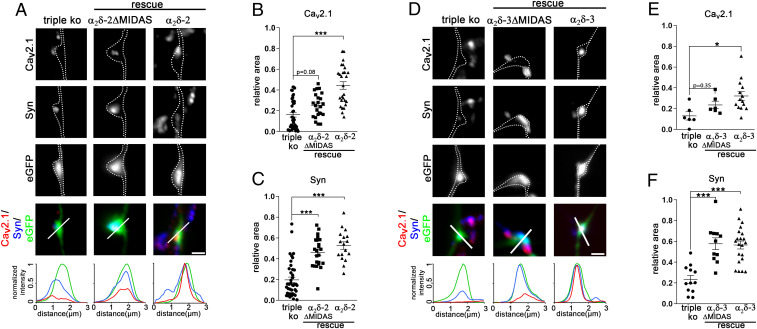
Fig. 7.
Rescuing triple-knockout/knockdown synapses with α2δ-2-ΔMIDAS or α2δ-3-ΔMIDAS dissociates synapse differentiation from presynaptic calcium channel trafficking. (A and D) Immunofluorescence micrographs of axonal varicosities from presynaptic α2δ TKO/KD neurons (triple KO, eGFP-positive axonal varicosities, Left) and neurons expressing α2δ-2-ΔMIDAS or α2δ-2 (A) and α2δ-3-ΔMIDAS or α2δ-3 (D). Axonal varicosities are outlined by a dashed line. Immunolabeling for CaV2.1 and synapsin (syn) revealed that, unlike α2δ-2 or α2δ-3, expression α2δ-2-ΔMIDAS or α2δ-3-ΔMIDAS in TKO/KD neurons fully rescued presynaptic synapsin but not CaV2.1 clustering. The relative fluorescence of each signal was recorded along the indicated line to support these observations. (B, C, E, and F) Quantification of the relative synaptic area covered by the respective immunofluorescence of presynaptic CaV2.1 (B and E) and synapsin (C and F) [ANOVA, α2δ-2: CaV2.1, F(2, 78) = 18.9, P < 0.001, n = 41 (triple KO), 23 (MIDAS), and 17 (rescue) from 3 to 10 culture preparations; synapsin, F(2, 56) = 18.7, P < 0.001, n = 19 (triple KO), 23 (MIDAS), and 17 (rescue) from three to four culture preparations; α2δ-3: CaV2.1, F(2, 23) = 4.7, P < 0.019, n = 6 (triple KO), 6 (MIDAS), and 14 (rescue) from two to three culture preparations; synapsin: F(2, 41) = 17.3, P < 0.001, n = 12 (triple KO), 11 (MIDAS), and 21 (rescue) from three to four culture preparations; Tukey post hoc test, *P = 0.016, ***P < 0.001; horizontal lines represent means and error bars SEM]. (Scale bars, 1 µm.)