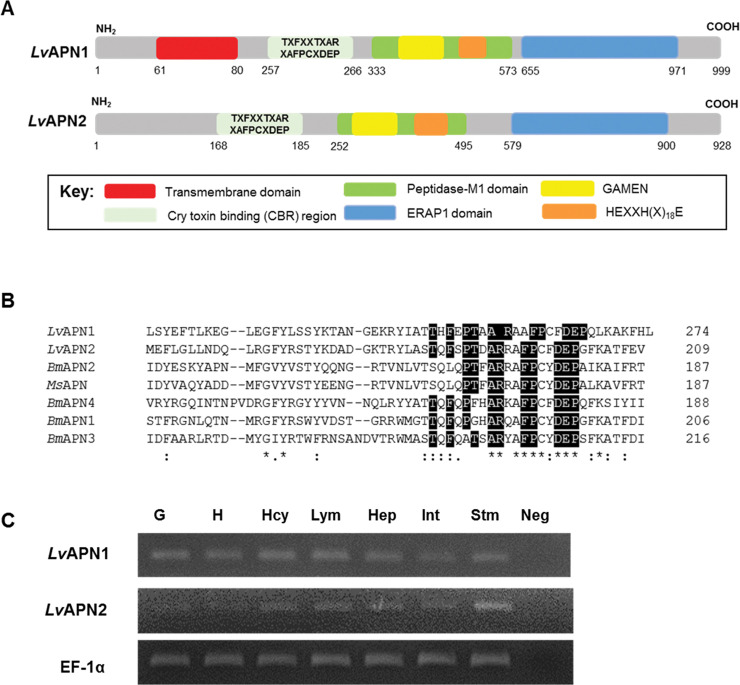
Fig 1. LvAPN1 characteristics analysis.
(A) Schematic presentation of specific motifs and other components in the LvAPN sequence. Predicted positions of the putative N-terminal transmembrane domain, Cry-binding region (CBR), peptidase-M1 domain, and the GAMEN and HEXXH(X)18E zinc-binding site motifs are shown in red, grey, green, yellow, blue and orange, respectively. (B) Alignment of the Cry1Aa toxin-binding region (CBR) of Litopenaeus vannamei, Bombyx mori and Manduca sexta APNs. The sequences of LvAPN1 (XP_027215499.1); LvAPN2 (XP_027218958.1); BmAPN1 (AFK85020); BmAPN2 (AB011497); BmAPN3 (AF352574); BmAPN4 (AB013400) and MsAPN (CAA66466) were compared. Perfectly conserved amino acid residues have black backgrounds. (C) Aminopeptidase N transcript expression analysis in various L. vannamei tissues by RT-PCR. The tissues examined were gill (G), heart (H), hemocyte (Hcy), lymphoid (Lym), hepatopancreas (Hep), intestine (Int) and stomach (Stm). EF1-α was used as the internal reference and PCR control. Neg is a negative control. A representative data of 3 biological replicates is shown.