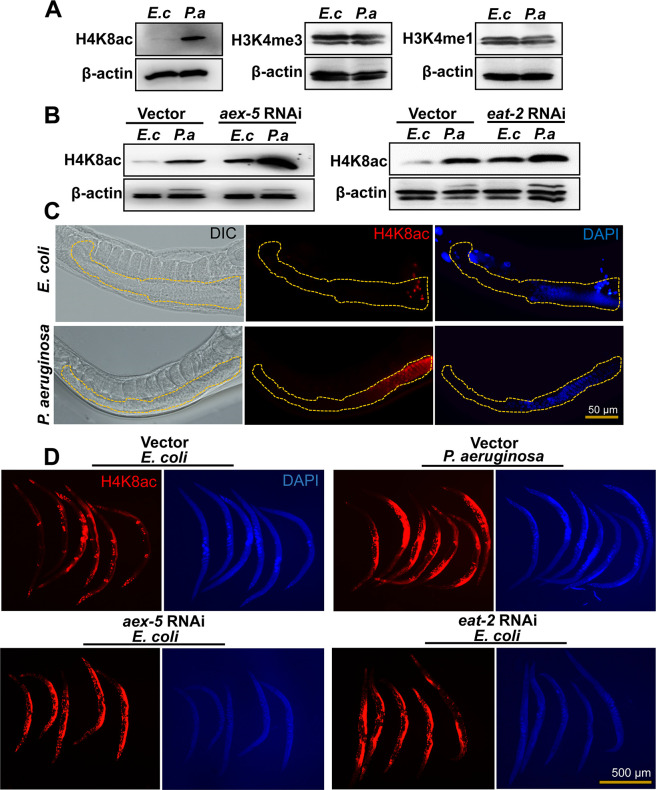
Fig 1. P. aeruginosa infection and intestinal distension induce H4K8ac in the germline.
(A) Western blots of extracts from fer-1(b232) animals exposed to E. coli (E. c) or P. aeruginosa (P. a) for 24 hours at 25°C (n ≈ 1,000; representative of 3 independent experiments). (B) Western blots on extracts from fer-1(b232) animals exposed to E. coli (E. c) or P. aeruginosa (P. a) following aex-5 and eat-2 RNAi for 24 hours at 25°C (n ≈ 1,000; representative of 3 independent experiments). The fer-1(b232) animals were maintained at 15°C. To induce sterility, L1-stage animals were transferred to 25°C and allowed to develop. L4-stage animals were then transferred to RNAi plates and allowed to grow for 24 hours at 25°C. “n” represents the number of animals for each experiment (A, B). (C) Representative microscopic images of portions of C. elegans germline depicting differences in H4K8ac patterns. Yellow-dotted lines were used to outline the germline. (D) Whole-mount immunofluorescence profile of wild-type animals stained with anti-H4K8ac antibody, post exposure to E. coli (E. c) or P. aeruginosa (P. a) following aex-5 and eat-2 RNAi for 24 hours at 25°C. See S1 Raw Images for uncropped immunoblot images. H4K8ac, histone H4 Lys8 acetylation; RNAi, RNA interference.