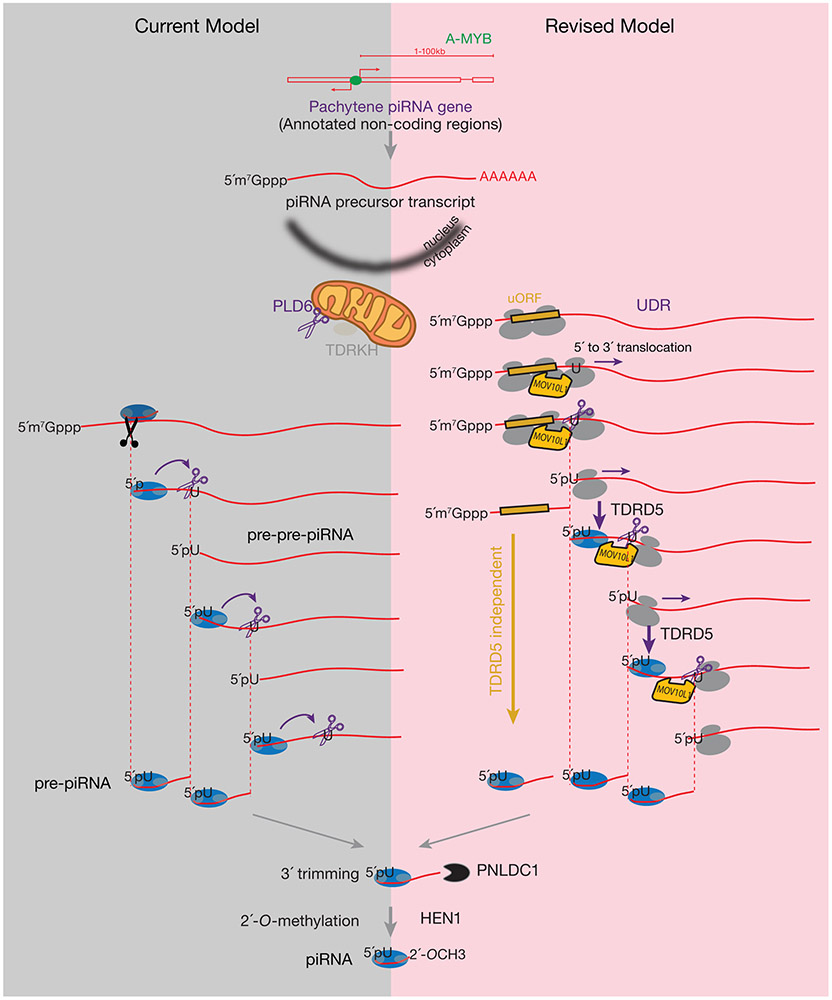
Extended Data Fig. 1. Comparison of the current model (left panel) of pachytene piRNA biogenesis and the revised model (right panel).
The grey bubbles represent the large and small subunits of ribosomes. The blue bubbles represent PIWI proteins. Grey circle in PIWI proteins on the left represents MID domain that recognizes the 5´-phosphate (5´P)70,71, on the right represents PAZ domain, in between represents PIWI domain. In both models, piRNA precursors are synthesized by RNA polymerase II, and contain the 5´-cap, exons, introns, and a poly(A) tail. The transcription of pachytene piRNA genes is controlled by A-MYB. The 5´-end-loaded PIWI proteins specify the endonuclease PLD6 cleavage site, determine the 5´- and 3´-ends of pre-piRNAs, and generate strings of head-to-tail phased piRNAs that will be further trimmed and methylated. In the revised model, ribosomes associate with precursors in a canonical fashion through initiating at the start codon near the 5´-cap. Facilitated by MOV10L1, ribosomes translate into the UDRs (Purple arrows). Ribosome-bound UDRs are targeted by PLD6-mediated cleavage. The cleavage of piRNA precursors upstream of the ribosome E site (at the exit site of the mRNA ribosome channel) does not prevent the ribosome from translating towards the 3´-end of the piRNA precursors. The cleavage machinery, generating 1U bias, appears to pause the ribosomes, leading to the detection of in vivo processed RPFs dwelling at future piRNA sites at the steady-state. As ribosomes translocate, they can release the 5´P of pre-pre-piRNAs for PIWI loading that guides stepwise phased piRNA production. piRNA biogenesis at the UDRs requires TDRD5 protein. Transcripts containing ORFs are translated by polysome, and they are processed to piRNAs in a distinct manner that does not require TDRD5 (Gold arrows).