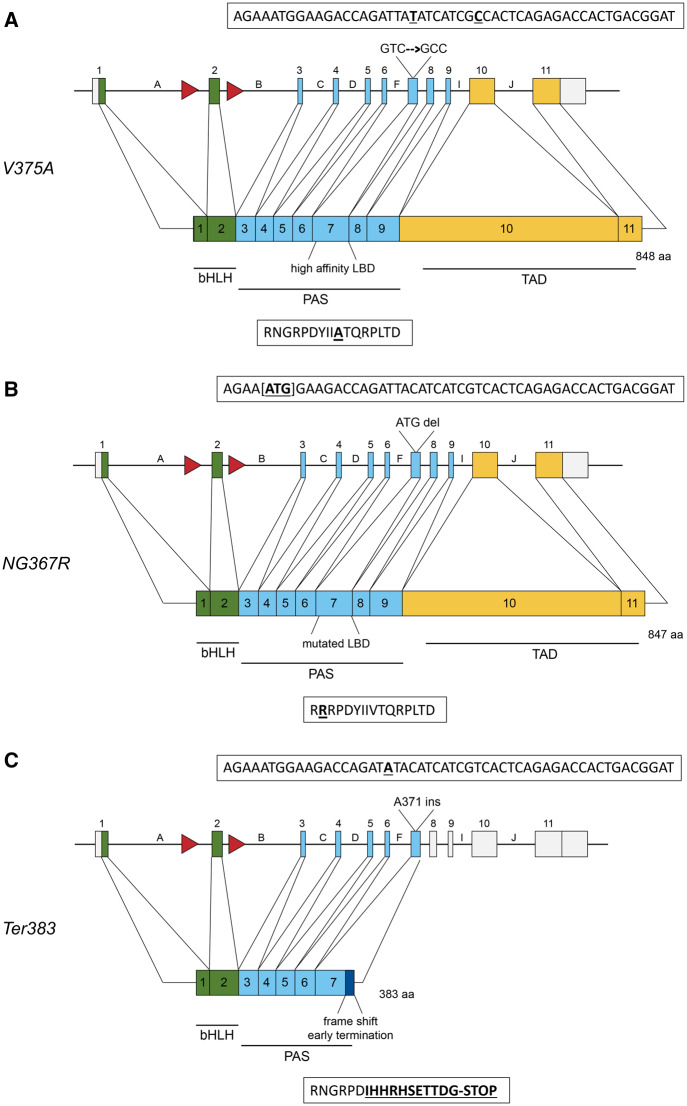
Figure 2.
Gene structure and protein map of induced mutations. Green boxes represent exons corresponding to amino acids in the bHLH domain, responsible for DNA binding and nuclear translocation. Blue boxes represent the PAS domain where dimarization with Ah Receptor Nuclear Translocator (ARNT) and ligand binding occur. Yellow boxes represents the transactivation domain. Red arrows represent IoxP sites flanking exon-2. Boxes above each allele show the DNA sequence; boxes below each allele describe the amino acid sequence. A, Protein map for the V375A allele. The gene encoded a point mutation at residue 375, changing GTC (Valine) to GCC (Alanine). The point mutation and silent mutation are shown bolded and underlined. B, Protein map for the NG367R allele. At the Ahr locus, 3 bp [ATG] were deleted, resulting in an amino acid deletion and substitution (NG367R), yielding a mutated PAS-B and ligand-binding domain. The deleted nucleotides are designated by brackets in the DNA sequence. The amino acid change is bolded and underlined. C, Protein map for the Ter383 allele based on genomic mutations. An adenine insertion at the codon for residue 371 in the gene resulted in a frame shift and early termination at residue 383. The dark blue box in the protien map represents amino acids following 371 that have been altered as a result of the frame shift. The adenine insertion and mutated amino acids are bolded and underlined.