Fig. 4 .
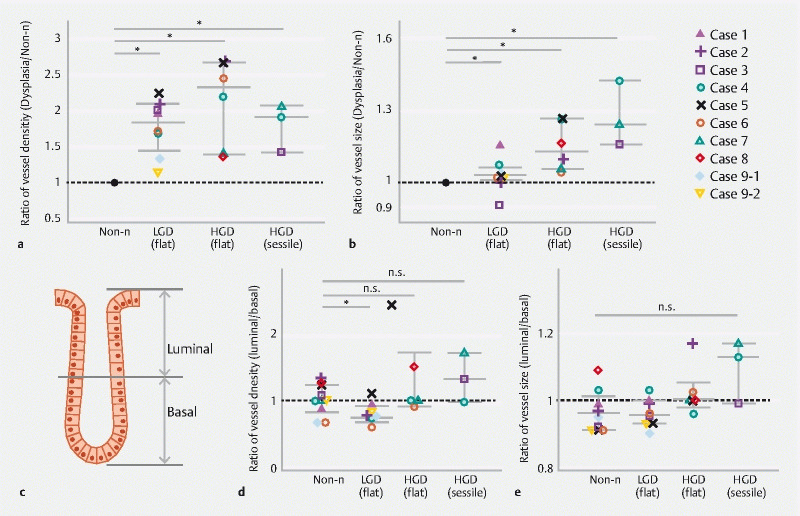
Evaluation of intramucosal vessel density/size in non-neoplastic, low-grade dysplasia and high-grade dysplasia. a Evaluation of intramucosal vessel density in non-neoplastic (Non-n) (n = 10), low-grade dysplasia (LGD) (n = 7), flat-type high-grade dysplasia (HGD) (n = 5) and sessile HGD lesions (n = 3). The ratio of average vessel density in LGD, flat-type HGD or sessile HGD lesions to that in Non-n lesions in each case is shown. b Evaluation of intramucosal vessel size in Non-n (n = 10), LGD (n = 7), flat-type HGD (n = 5) and sessile HGD lesions (n = 3). The ratio of average vessel size in LGD, flat-type HGD or sessile HGD lesions to that in Non-n lesions in each case is shown. c Schematic presentation showing the separation of colonic crypts and their surrounding stroma into the luminal and basal half areas. d Evaluation of vessel density in the luminal and basal half areas of Non-n (n = 10), LGD (n = 7), flat-type HGD (n = 5) and sessile HGD lesions (n = 3). The ratio of average vessel density in the luminal half areas to that in the basal half areas in each case is shown. E. Evaluation of vessel size in the luminal and basal half areas of Non-n (n = 10), LGD (n = 7), flat-type HGD (n = 5) and sessile HGD lesions (n = 3). The ratio of average vessel density in the luminal half areas to that in the basal half areas in each case is shown. A Mann-Whitney U test was performed. * P < 0.05.
