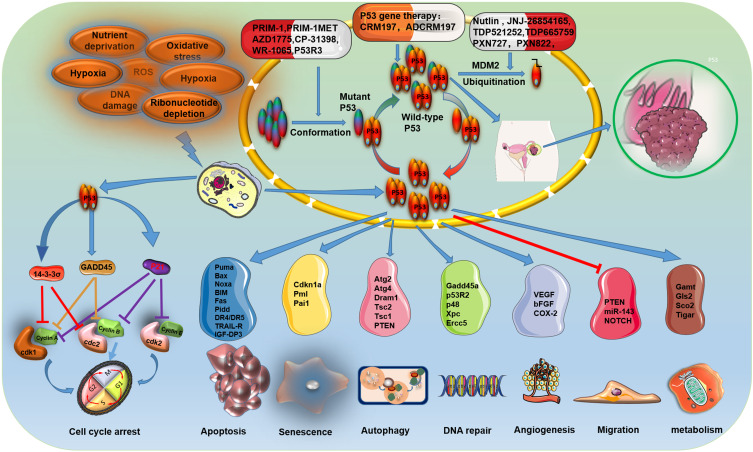
Figure 2.
Cellular functions of P53 in ovarian cancer. P53 is activated to regulate the expression downstream genes to induce a series of cellular responses, such as cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, senescence, autophagy, DNA repair, angiogenesis, migration and metabolism in different types of extracellular and intracellular stress (eg, nutrient deprivation, telomere erosion, hypoxia, DNA damage, ribosomal stress, and oncogene activation). The primary treatment strategy for patients with ovarian cancer with P53 mutations is focused on restoring WT-P53 function to mutant P53, Blocking the interaction of WT P53 with MDM2/MDM4, and gene therapy with P53.