Fig. 1. The WENGAN algorithm.
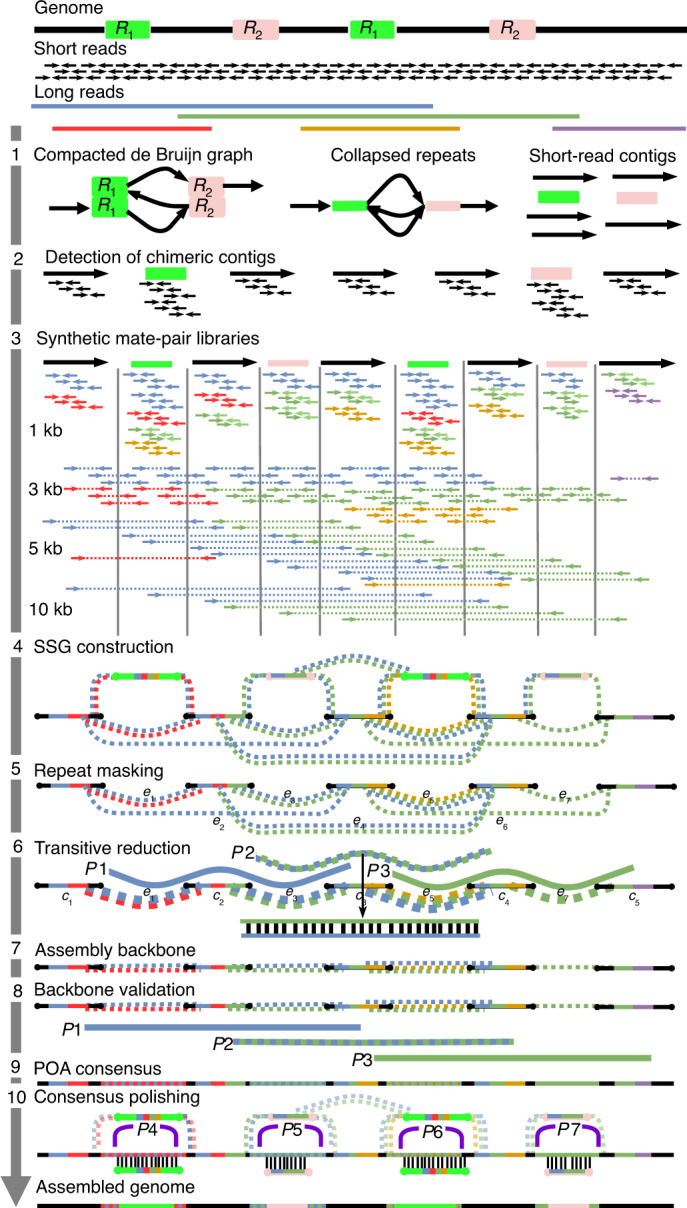
The WENGAN workflow consists of first assembling and error-correcting the short-read contigs (1 and 2), creating a spectrum of synthetic mate-pair libraries from long reads (3) and building of the SSG (4). The SSG is used to compute approximate long-read overlaps by building long-read-coherent paths (5 and 6). The long-read overlaps restore the long-read information and facilitate the construction and validation of the assembly backbone (7 and 8). The SSG is used to fill the gaps by building for each mate edge a consensus sequence using the partial order alignment graph (9). In the final step, the SSG is used to polish the consensus sequences (10). The repeat contigs (2–10) are drawn uncollapsed to explain the WENGAN steps.
