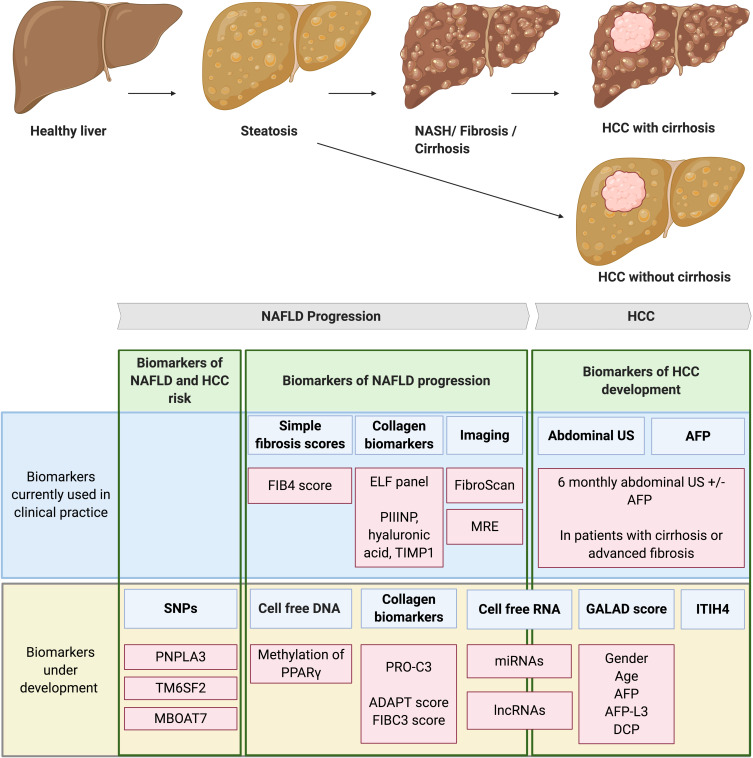
Figure 2.
Biomarkers of NAFLD progression and HCC development. NAFLD is a spectrum of liver disease ranging from steatosis to NASH, fibrosis and eventually cirrhosis. HCC mainly develops on the background of liver cirrhosis however between 25–50% of HCC develops in the absence of cirrhosis. Biomarkers of NAFLD and HCC risk. SNPs in PNPLA3, TM6SF2 and MBOAT7 genes are associated with both NAFLD progression and the development of NAFLD-HCC. TM6SF2 in particular is an independent risk factor for HCC development in the absence of cirrhosis. The predictive values of these SNPs are insufficient to be used in clinical practice on their own, however risk stratification tools may be developed using combinations of SNPs. Biomarkers of NAFLD progression. Biomarkers currently used in clinical practice to detect NAFLD fibrotic progression include; simple fibrosis scores such as the FIB4 score, panels using collagen biomarkers such as the ELF panel and imaging techniques such as FibroScan and MRE. Biomarkers currently under development include; PPARγ methylation of cell-free DNA, scoring systems using the PRO-C3 collagen neo-epitope (ADAPT and FIBC3) and circulating cell-free RNA. Biomarkers of HCC development. Current clinical guidelines recommend screening for HCC development with 6-monthly abdominal US with or without AFP measurements in patients with cirrhosis or advanced fibrosis. Biomarkers being developed to better detect HCC include; the GALAD score, measurement of serum ITIH4 and detection of cell-free RNA. Created with BioRender.com.
Abbreviations: AFP, alpha-fetoprotein; AFP-L3, alpha-fetoprotein L3; DCP, des-gamma-carboxy-prothrombin; ELF, enhanced liver fibrosis; FIB4, fibrosis-4; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; ITIH4, inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 4; lncRNAs, long non-coding RNAs; MBOAT7, membrane-bound 0-acyltransferase domain containing 7; miRNAs, micro non-coding RNAs; MRE, magnetic resonance elastography; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; PNPLA3, patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3; PIIINP, type III procollagen peptide; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferation-activated receptor gamma; PRO-C3, N-terminal type III collagen propeptide; SNPs, single nucleotide polymorphisms; TIMP1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1; TM6SF2, transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2; US, ultrasound.