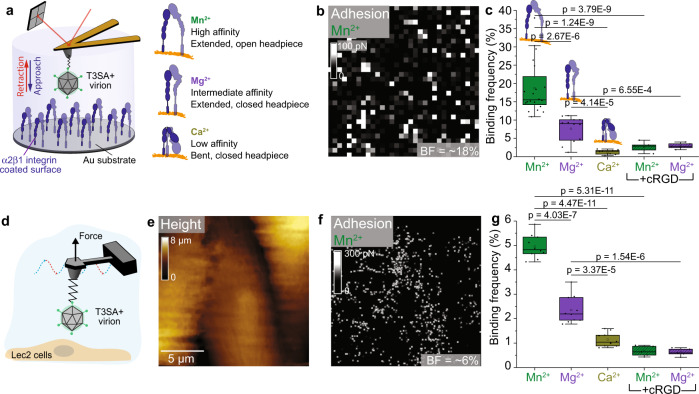
Fig. 2. Reovirus directly engages β1 integrins in a cation-dependent manner.
Studies were conducted using model surfaces (a–c) and living cells (d–g). a Experimental set up (left) to probe cation-dependent (right) virion-α2β1 integrin interactions using a model surface. b The adhesion map shows interaction forces (white pixels) between virions and integrins in the presence of Mn2+, which induces an extended integrin conformation. c Box plot of specific binding frequencies (BF) measured using AFM between virions and integrins in the presence of divalent cations and following injection of cRGD. d FD-based AFM setup to study T3SA+ binding to Lec2 cells, which express β1 integrins. Height (e) and corresponding adhesion maps (f) of the imaged area show specific binding of reovirus T3SA+ to living Lec2 cells in the presence of Mn2+ (white pixels). For better visibility, the pixel size in the adhesion image was enlarged two-fold. AFM images were acquired using an oscillation frequency of 0.25 kHz and amplitude of 750 nm under cell culture conditions. g Box plot shows BF of T3SA+ virions to β1 integrins on living Lec2 cells under conditions shown. The horizontal line within the box indicates the median, boundaries of the box indicate the 25th and 75th percentile, and whiskers indicate the highest and lowest values. Open square within each box indicates the mean. All data are representative of N = 5 independent experiments. P values were determined by two-sample t-test using Origin.