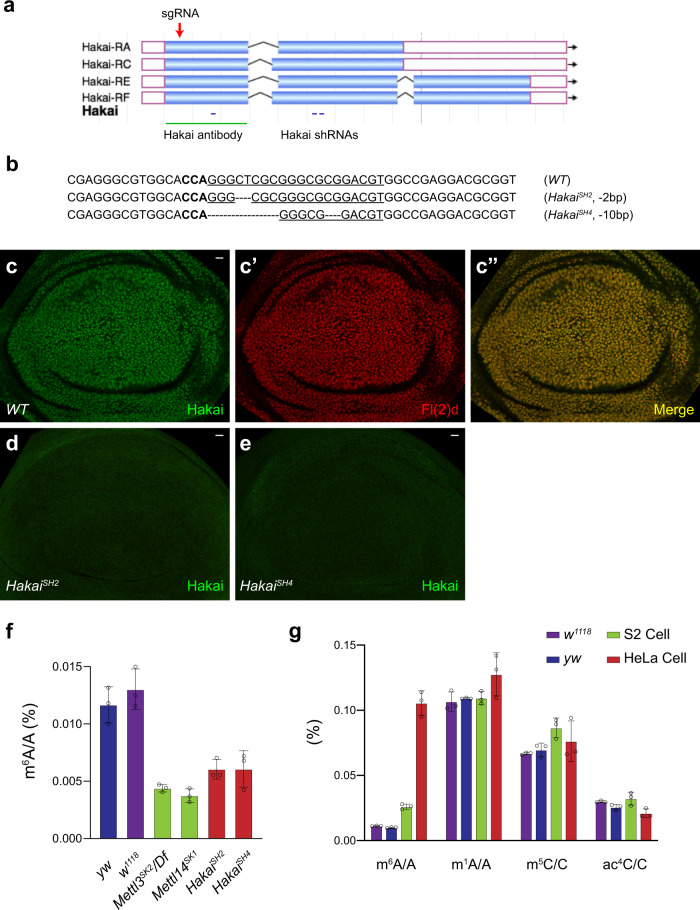
Fig. 2. Hakai is required to maintain proper levels of m6A methylation.
a Flybase JBrowse view of the Hakai gene locus. Hakai has four transcripts due to alternative splicing that generates two long and two short protein isoforms. The positions of three independent shRNAs, Hakai sgRNA, and the protein region used to generate a Hakai antibody are indicated. b Sequencing results showing frameshift indels in HakaiSH2 and HakaiSH4 flies generated by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutagenesis. The targeted genomic DNA sequence is underlined and the NGG PAM sequence is in bold type. c–c” Hakai and Fl(2)d antibody staining in WT wing discs showing a high degree of co-localization. Hakai antibody staining was strongly reduced in HakaiSH2 (d) or HakaiSH4 (e) homozygous mutant wing discs. The experiments in c–e were repeated at least twice independently with similar results, and each time around 30 wing discs for any genotype were examined. Scale bars: 10 μm. f Quantifications of m6A relative to A in mRNA extracted from male adult flies by LC-MS. Compared to yw and w1118 controls, m6A levels dropped to about 30% in Mettl3 or Mettl14 mutants and to <50% in HakaiSH2 or HakaiSH4 mutants. g Quantifications of m6A/A, m1A/A, m5C/C, and ac4C/C levels in mRNA extracted from yw and w1118 male flies, Drosophila S2 cells, and human HeLa cells. Note the substantial difference between fly and human m6A levels. f, g Data are presented as mean ± SD from three biological replicates. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.