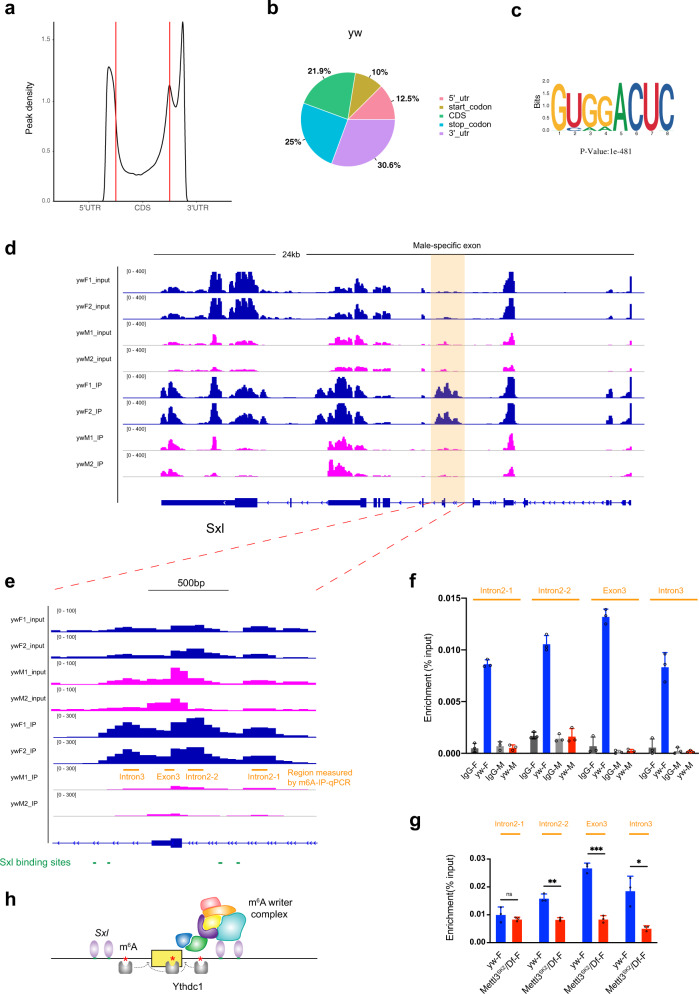
Fig. 6. Female-specific deposition of m6A on the Sxl mRNA.
a MeRIP-seq shows that the normalized density of m6A peaks across 5′UTR, CDS, and 3′UTR of mRNA in yw male adult flies. b Pie charts depicting m6A peak distribution in different transcript segments in yw flies. c Sequence motif identified from m6A peaks in yw flies by HOMER program. d Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) tracks displaying MeRIP-seq (lower panels, IP) and RNA-seq (upper panels, input) reads along Sxl locus in yw male (ywM) and female flies (ywF). Two replicates are shown. The region around male-specific exon3 is shaded and enlarged in (e) highlighting 3–4 m6A peaks on and around exon3 only in female flies. Adjacent Sxl-binding sites are also shown. f m6A-IP-qPCR showing enrichments over Sxl mRNA in yw male or female flies IPed with m6A or IgG antibody. Regions measured are indicated in (e). g m6A-IP-qPCR showing enrichments over Sxl mRNA in yw or Mettl3SK2/Df female flies IPed with m6A antibody. Data are presented as mean ± SD from three biological replicates. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; ns not significant, two-sided unpaired t test. In g, P = 0.3679, 0.0012, 0.0001, 0.0114. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. h A working model on how the m6A modifications cooperate with Sxl to regulate its mRNA splicing.