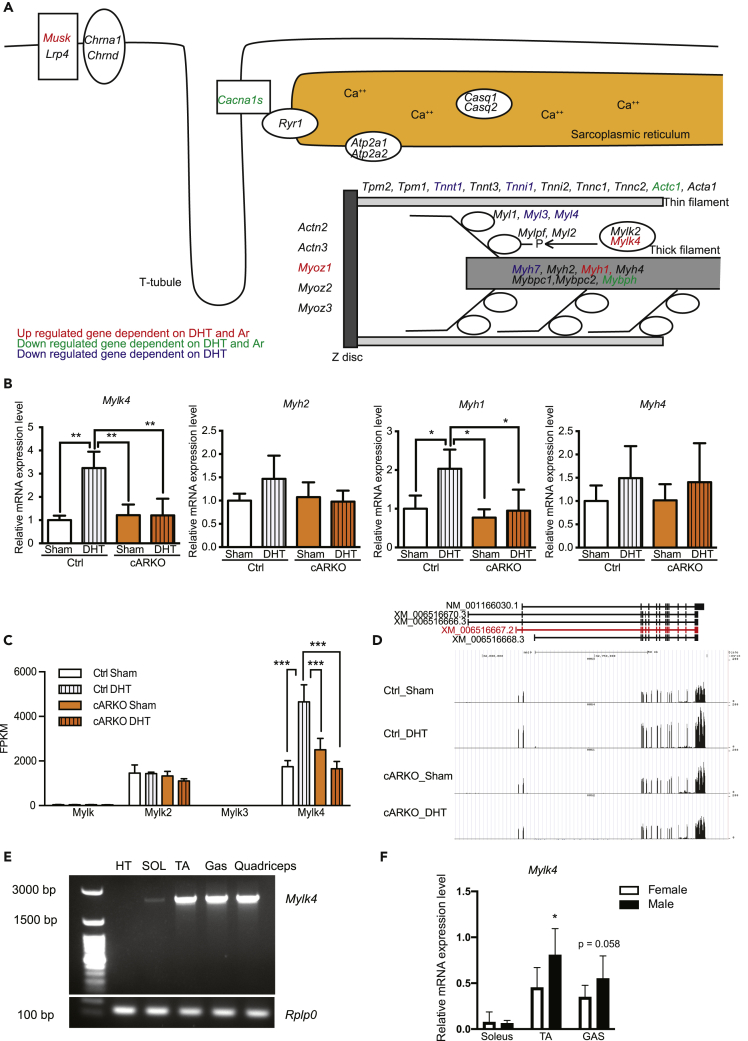
Figure 3.
AR induced skeletal muscle-specific splicing variant of Mylk4 gene expression
(A) A muscle sarcomere model showing AR- and DHT-dependent upregulated or downregulated genes.
(B) mRNA expression levels of Mylk4, Myh2, Myh1, and Myh4 in gastrocnemius muscles of 13-week-old female Control_Sham (n = 4), Control_DHT (n = 3), cARKO_Sham (n = 4), and cARKO_DHT (n = 5) mice. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001.
(C) FPKM (fragments per kilobase of exon per million reads mapped) values of Mylk genes.
(D) Schematic image of Mylk4 gene locus.
(E) Real-time-PCR analysis of skeletal muscle-specific splicing variants of Mylk4.
(F) Mylk4 gene expression was determined in soleus muscles, TA muscles, and gastrocnemius muscles of male or female mice by RT-qPCR (n = 8, each tissue). Data are represented as mean ± standard deviation. ∗P < 0.05. One-way analysis of variance followed by Student Newman-Keuls tests.
See also Figures S4 and S5.