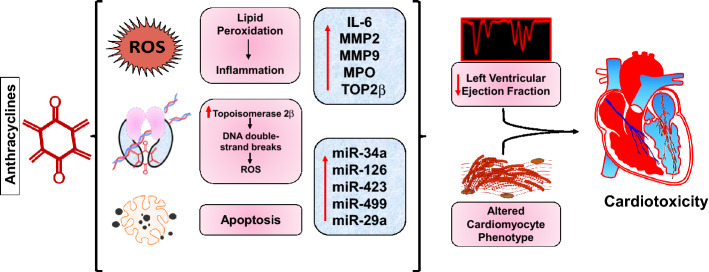
Figure 7.
Schematic representation of anthracyclines induced cardiotoxicity. The treatment of breast cancer patients with an anthracycline regimen results in excessive ROS production with subsequent oxidant stress and inflammation in the cardiomyocyte. Anthracycline treatment also results in double strand DNA damage as well as cellular apoptosis which further contributes to the cardiotoxicity. The upregulation of biomarkers and circulating miRNAs associated with these pathological mechanisms operant in response to anthracycline treatment contributes to a decline in LVEF and altered cardiomyocytes, hence predicting early cardiotoxicity events.