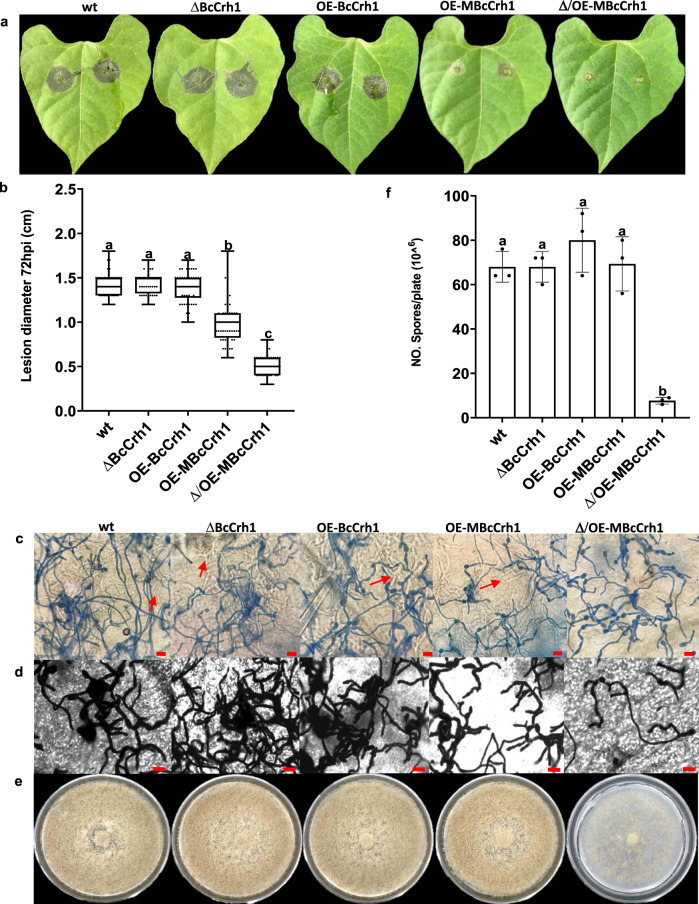
Fig. 6. Over expression of MBcCrh1 causes reduced pathogenicity and developmental defects.
a–b Infection assay. Bean leaves were inoculated with spore suspensions of B. cinerea wild type (wt), bccrh1 deletion (ΔBcCrh1), bccrh1 overexpression (OE-BcCrh1), and strains over-expressing the enzyme inactive (MBcCrh1) protein in wild type (OE-MBcCrh1) or bccrh1 deletion (Δ/OE-MBcCrh1) genetic background. Symptoms were photographed and the lesion diameter was recorded 72 hpi. Box limits show the 25th and 75th percentiles. The center lines of boxplots indicate the medians values; whiskers extend to minimum and maximum values from the 25th and 75th percentiles; all data are indicated as black dots. At least 40 sample points from three independent biological replicates were used for statistical analysis. c–d Lactophenol cotton blue and lactophenol trypan blue staining of infected leaves. Leaf tissue was harvested at the designated time points and stained with lactophenol cotton blue, which stains only the exposed hyphae (c), and with lactophenol trypan blue, which stains both exposed and intracellular (red arrows) hyphae (d). Bar = 20 μm. Note the near absence of intracellular hyphae in the Δ/OE-MBcCrh1 mutant, which indicates penetration defects. All the experiments were repeated three times with similar results. e–f Mycelium and spore production. Fungi were cultured on solid GB5-Glucose medium and grown at 20 °C with continuous light. Pictures were taken (e) and spores counted after eight days of incubation. Data represent mean ± SD from three independent biological replicates. Different letters in (b) and (f) indicate statistical differences at P ≤ 0.01 according to one-way ANOVA.