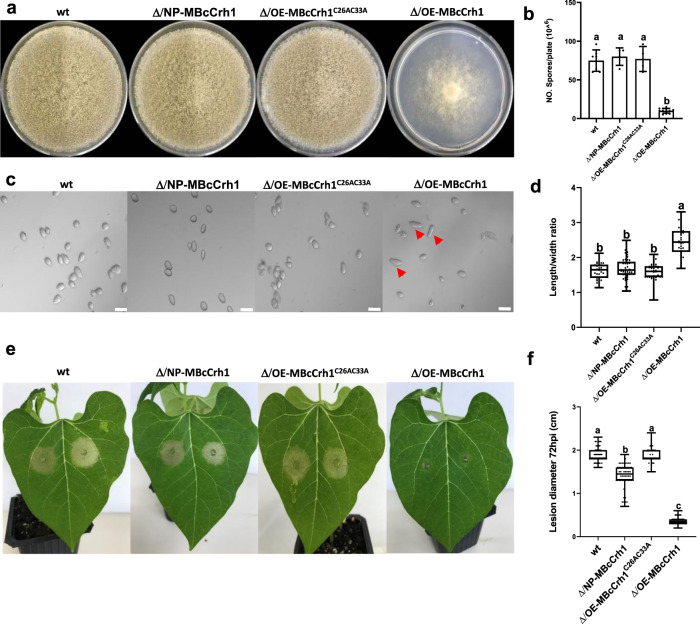
Fig. 7. The pathogenicity and developmental defects induced by MBcCrh1 depend on expression levels.
The following strains were characterized: B. cinerea wild type (wt), enzyme inactive BcCrh1 with the native promoter in the background of bccrh1 deletion (Δ/NP-MBcCrh1), overexpression of MBcCrh1 with mutation of C26 and C33 in a background of bccrh1 deletion (Δ/OE-MBcCrh1C26AC33A), and overexpression of MBcCrh1 in a background of bccrh1 deletion (Δ/OE-MBcCrh1). a–d Spore production and shape. Fungi were cultured on solid GB5-Glucose medium and grown at 20°C with continuous light. Pictures of plates (a) and spores (c) were taken after eight days of incubation. Spores were harvested and average spore numbers (b) and spore dimensions (d) were determined. Arrows indicate spores of the Δ/OE-MBcCrh1 strain with abnormal morphology. For spore numbers, data represent mean ± SD from three independent biological replications. For spore dimensions, the ratio of length/width was calculated. Data of at least 30 spores from three independent biological replications were used for statistical analysis. e–f Bean leaves were inoculated with spore suspensions of the different strains, pictures were taken and lesion size recorded 72 hpi. At least 32 sample data from three independent biological replications were used for statistical analysis. In boxplots (d and f), center lines represent the medians, box edges show the 25th and 75th percentiles; whiskers extend to minimum and maximum values from the 25th and 75th percentiles; all present data are indicated as black dots. Different letters in d and f indicate statistical differences at P ≤ 0.01 according to one-way ANOVA.