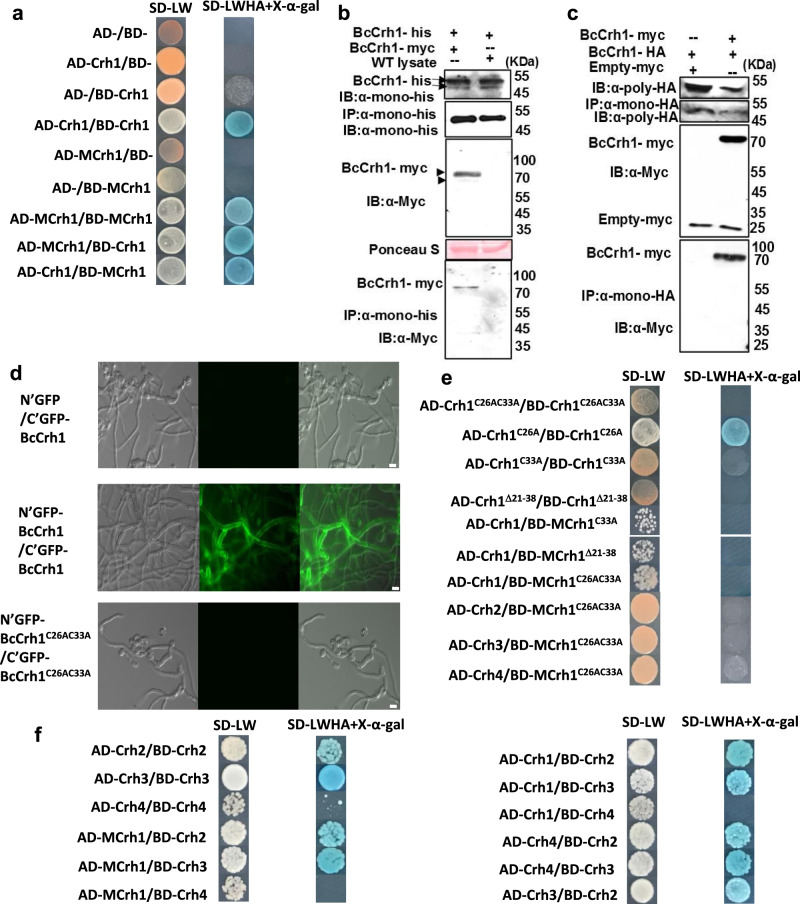
Fig. 8. BcCrh protein dimerization.
a Yeast two-hybrid assay (Y2H) of BcCrh1 and MBcCrh1 homodimer formation. SD/-Trp-Leu medium was used to confirm the transformation events. SD/-Trp-Leu-His-Ade medium containing X-α-gal was used to screen yeast strains with the positive protein-protein interaction. b–d Confirmation of BcCrh1 dimer formation by in vitro pull down assay (b), Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assay (c) and bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assay (d). b For the in vitro pull-down assay, BcCrh1-myc was transiently expressed in N. benthamiana and pull down was performed with BcCrh1-His recombinant protein conjugated with histidine beads. Protein from non-infiltrated leaves (WT lysate) was used as negative control. c For the Co-IP experiment, BcCrh1-myc or empty-myc were co-expressed with the BcCrh1-HA in N. benthamiana. BcCrh1-myc, but not empty-myc, co-immuno-precipitated with BcCrh1-HA conjugated to HA beads. c BiFC was conducted with B. cinerea transgenic strain expressing split GFP-BcCrh1 proteins (N′GFP-BcCrh1/C’GFP-BcCrh1). A strain expressing split GFP fused to BcCrh1C26AC33A (N’GFP-BcCrh1C26AC33A/C′GFP-BcCrh1C26AC33A) did not show any fluorescence, indicating a lack of dimer formation by this protein derivative. Bar = 10 μm. The experiments were repeated three times with similar results. e Effect of point mutations or deletion at the N’ part of BcCrh1 on homo- and heterodimer formation. f Y2H assay of interaction between different BcCrh members.