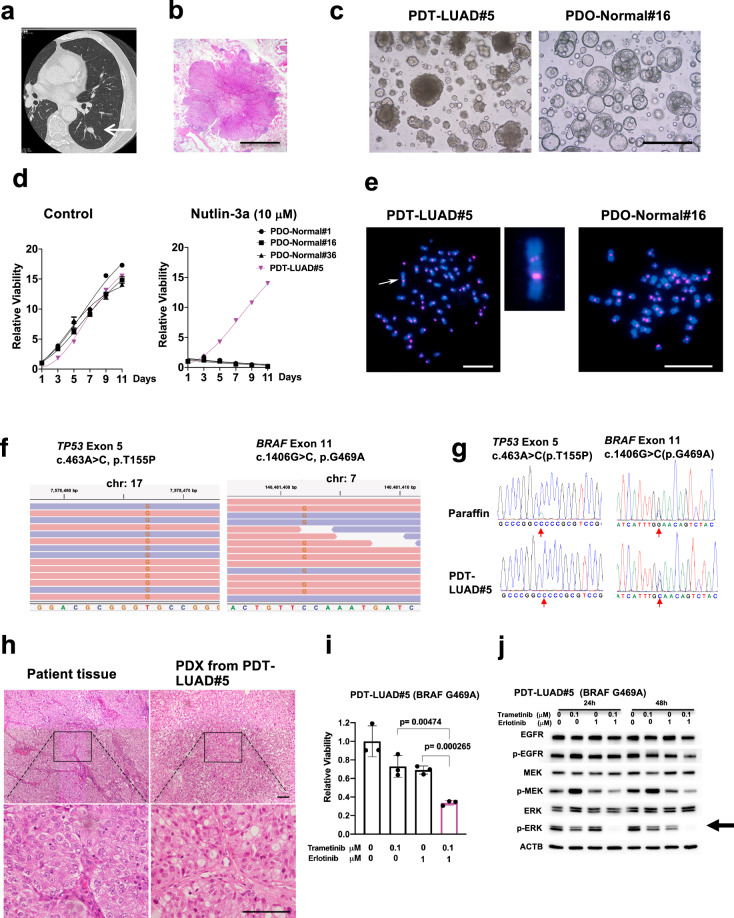
Fig. 1. Patient-derived tumoroids (PDTs) from early stage primary lung cancer with a BRAF mutation (PDT-LUAD#5).
a The nodule located in the left lower lobe was found by a CT scan (white arrow). b Lung cancer with lobulated edges is shown in Loupe view by hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining. Scale bar, 5 mm. c Shown are bright-field microscopy images of PDT-LUAD#5 and PDO-Normal#16. Scale bar, 500 μm. d Cell viability assays on tumoroids or organoids were conducted over 11 days with or without nutlin-3a (10 μM). Lung tumoroids (PDTs) and normal lung organoids (PDOs) were seeded into 96-well white polystyrene plates at a density of 1 × 103 cells with 4 μl of Cultrex growth factor reduced BME type 2 (Matrigel) per well 24 h before treatment. Cell viability assay was performed as described in the Methods section. e Shown are metaphase FISH images of PDT-LUAD#5 and PDO-Normal#16. An aberrant chromosome indicated by a white arrow was seen in PDT-LUAD#5. No chromosome abnormalities are seen in PDO-Normal#16. Scale bars, 20 μm. f Exome-seq detected a biallelic TP53 c.463A > C (p.T155P) mutation and monoallelic BRAF c.1406G > C (p.G469A) mutation from PDT-LUAD#5. Red and blue lines represent forward and reverse reads, respectively. g Sanger sequencing confirmed the TP53 and BRAF mutations seen in f in DNA from both paraffin-embedded parental tissue and lung tumoroids (PDT-LUAD#5). h Shown are HE stained images of the parental lung cancer tissue (left) and the PDX (patient-derived xenografts) derived from PDT-LUAD#5 (right) (magnified in lower image). Scale bar, 100 μm. i Combination treatment of trametinib and erlotinib significantly suppressed the viability of PDT-LUAD#5 72 h after treatment. Cell viability assay was performed as described in d. Data are shown as mean ± SD. j The combination treatment of trametinib and erlotinib suppressed phosphorylation of ERK (arrow) both 24 and 48 h after treatment.