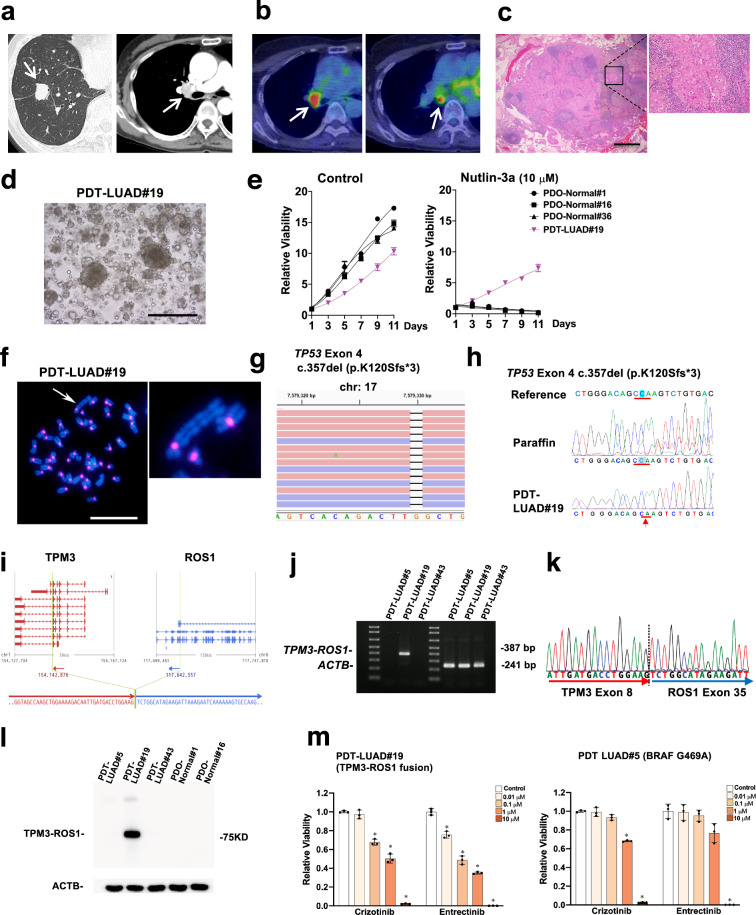
Fig. 2. Patient-derived tumoroids (PDTs) from lymph node metastasis of a metastatic lung cancer (PDT-LUAD#19).
a The nodule located in the right lower lobe was found by a CT scan (white arrow, left column). Enlarged right hilar lymph node was detected by Contrast Enhanced Computed Tomography (CECT) (white arrow, right column). b Increased FDG uptake in hilar (left) and subcarinal (right) lymph nodes was observed by FDG-PET/CT (white arrow). c Malignant cells were detected in the subcarinal lymph node specimen by HE staining (magnified on the right). Scale bar, 1 mm. d Shown is a bright-field microscopy image of PDT-LUAD#19. Scale bar, 500 μm. e Cell viability assays were conducted as described in Fig. 1d. f Metaphase FISH images are shown as described in Fig. 1e. An aberrant large chromosome was detected (white arrow). Scale bar, 20 μm. g Exome-seq detected c.357del (p.K120Sfs*3) and c.91G > A (p.V31I) (not shown) in both alleles of TP53 from PDT-LUAD#19. Red and blue lines represent forward and reverse reads, respectively. h Sanger sequencing confirmed the exome-seq data shown in Fig. 2g. i RNA-seq detected a TPM3-ROS1 fusion from PDT-LUAD#19. The junction of the two genes was located in chr1:154,142,876 and chr6:117,642,557. j RT-PCR confirmed the expression of a TPM3-ROS1 transcript in PDT-LUAD#19. ACTB was used as internal control. k Sanger sequencing result of a RT-PCR product from PDT-LUAD#19 harboring a TPM3-ROS1 rearrangement was consistent with the RNA-seq result. l TPM3-ROS1 fusion protein was detected using ROS1 antibody in PDT-LUAD#19. ACTB was used as internal control. m ROS1 inhibitors (crizotinib and entrectinib) significantly suppressed the growth of PDT-LUAD#19 (TPM3-ROS1; TP53K120Sfs*3) at lower concentration than that of PDT-LUAD#5 (BRAFG469A; TP53T155P) 72 h after treatment. Cell viability assays were performed as described in Fig. 1d. Data are shown as mean ± SD.