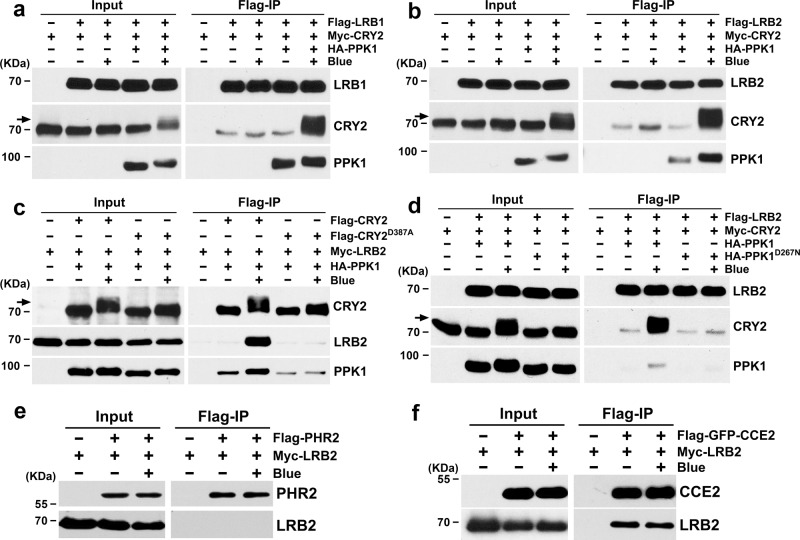
Fig. 3. LRBs interact with phosphorylated CRY2 in the HEK293T cells.
a Co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) assays showing the blue light and phosphorylation-dependent interaction of LRB1 and CRY2 in heterologous HEK293T cells. Immunoprecipitations (IP) were performed with Flag-conjugated beads. The IP (LRB1) and co-IP (CRY2) products were detected with anti-Flag and anti-CRY2 antibodies, respectively. PPK1 was detected with anti-HA antibody. b Co-IP assays showing the blue light and phosphorylation-dependent interaction of LRB2 and CRY2 in HEK293T cells. The experiments were performed as in (a). c Co-IP assays showing that LRB2 failed to interact with the photo-insensitive CRY2D387A mutant. The experiments were performed as in (a), except that the IP (CRY2 and CRY2D387A) and co-IP (LRB2) products were detected with anti-CRY2 and anti-Myc antibodies, respectively. d Co-IP assays showing the phosphorylation-dependent interaction of LRB2 and CRY2 interaction in HEK293T cells. The experiments were performed as in (a). PPK1D267N, catalytically inactive PPK1. e–f Co-IP assays showing the interaction between CRY2 CCE domain and LRB2. IP was performed with Flag-conjugated beads. The IP (PHR2 and CCE2) and co-IP (LRB2) products were detected with anti-Flag and anti-Myc antibodies, respectively. PHR2, photolyase homologous region of CRY2; CCE2, CRY2 C-terminal extension. The cells were treated with blue light (+ Blue; 100 μmol m−2 s−1) for 2 h or kept in the dark (-Blue). Arrows show phosphorylated CRY2. The above experiments were repeated three times with similar results.