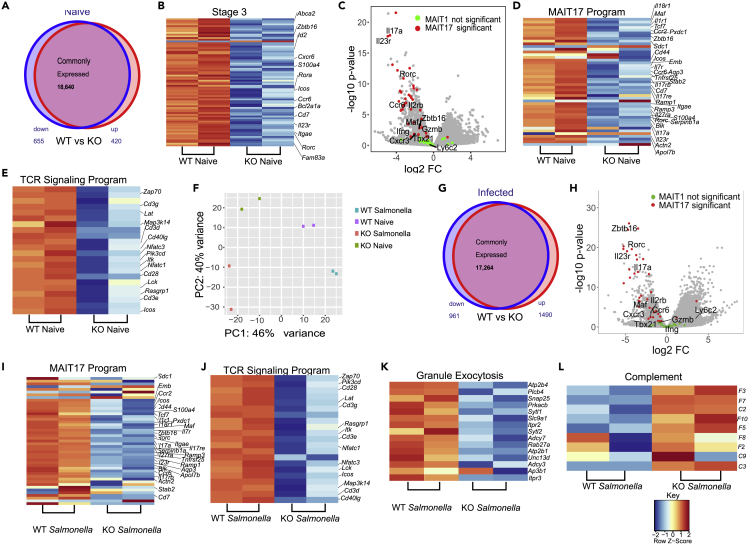
Figure 5.
Bcl11b sustains MAIT17, TCR signaling and cytotoxic granule exocytosis programs but represses complement genes in MAIT cells
All RNA-seq experiments were performed on sorted lin-TCRβ+MR1t-5-OP-RU+ MAIT cells from lung of Bcl11bF/F/PLZFcre/R26R-EYFP mice and WT control mice at steady state (A-F) or infected with Salmonella Typhimurium BRD509 (Salmonella) intranasally, day 7 post-infection (F-L). For Bcl11bF/F/PLZFcre/R26R-EYFP mice, in addition to lin-TCRβ+ MR1t-5-OP-RU+, sorting was conducted on YFP+ cells.
(A) Venn diagram depicting differentially expressed genes (significantly downregulated in blue and significantly upregulated in red) in Bcl11b KO and WT MAIT cells from uninfected mice.
(B) Heatmaps of differentially expressed stage 3 genes.
(C) Volcano plot of MAIT1 and MAIT17 genes in Bcl11b KO versus WT MAIT cells from mice at steady state.
(D) Heatmap of differentially expressed MAIT17 program.
(E) Heatmap of differentially expressed TCR signaling program genes in Bcl11b KO and WT MAIT cells from lung of uninfected mice. (n = 2).
(F) Principal component analysis (PCA) of MAIT cell RNA-seq from lung of Bcl11bF/F/PLZFcre/R26R-EYFP and WT mice at steady state or infected with Salmonella. (n = 2).
(G) Venn diagram depicting differentially expressed genes (significantly downregulated in blue and significantly upregulated in red) from Bcl11b KO and WT MAIT cells from Salmonella-infected mice.
(H) Volcano plot of MAIT17 and MAIT1 cells in Bcl11b KO versus WT MAIT cells from lung of mice infected with Salmonella.
(I–L) Heatmaps of MAIT17 program (I), TCR signaling (J), cytotoxic granule exocytosis (K) and complement (L) genes differentially expressed in Bcl11b KO and WT MAIT cells from Salmonella-infected mice. (n = 2). False discovery rate (FDR)–adjusted p values were calculated using the Benjamini-Hochberg method, with a significance cutoff of adjusted p < 0.05.