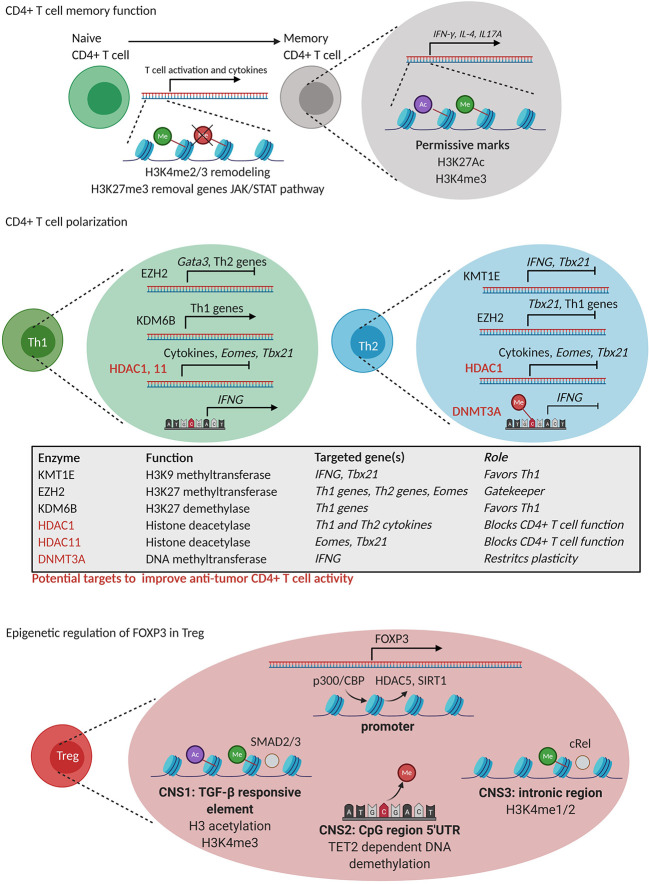
Figure 4.
Epigenetic regulation of CD4+ T cell differentiation. CD4+ T cell memory formation: During memory formation, remodeling of H3K4 methylation (green) marks takes place together with the removal of repressive H3K27me3 (red) marks in genes of the JAK-STAT pathway. Moreover, permissive H3K4me3 (green) and H3K27Ac (purple) marks are present in genes related to CD4+ T cell function. CD4+ T cell polarization: TH1 polarization is controlled by EZH2 that silences TH2-related genes and vice versa. KDM6B favors TH1 polarization by positive regulation of TH1-related genes while KMT1E negatively regulates IFNG and Tbx21 (T-bet) gene expression. HDAC1 and 11 are general inhibitors of CD4+ T cell function through silencing of cytokine production, Eomes and Tbx21 (T-bet). Epigenetic regulation of FOXP3 expression in Treg: FOXP3 expression is regulated by epigenetic processes in Treg including (i) exchange of repressive HDAC5 and SIRT 1 for a permissive CPB/p300 (HAT) complex, (ii) permissive H3K4me3 (green) and H3 lysine acetylation (purple) in a TGFβ response element (CNS1), (iii) TET2 dependent DNA demethylation of a 5’UTR region (CNS2), and (iii) H3K4me1/2 poised state of CNS3 needed for Foxp3 expression. HDAC1, 11 and DNMT3A represent potential targets to improve CD4+ T cell anti-tumor immunity.