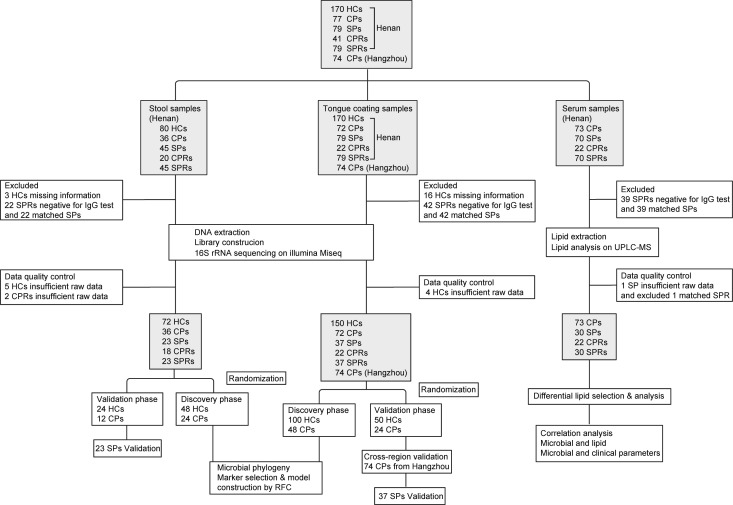
Figure 1.
Study design and flow diagram. A total of 957 samples of 3 types from Central China and East China were collected prospectively, including 496 tongue-coating samples, 226 faecal samples and 235 serum samples. After rigorous inclusion and exclusion criteria, 719 samples were included for further analysis, including 392 tongue-coating samples (72 CPs, 37 SPs, 22 CPRs, 37 paired SPRs and 150 HCs from Henan and 74 CPs from Hangzhou), 172 faecal samples (36 CPs, 23 SPs, 18 CPRs, 23 SPRs and 72 HCs from Henan) and 155 serum samples (73 CPs, 30 SPs, 22 CPRs and 30 SPRs). Oral and faecal samples were sequenced using 16S rRNA MiSeq to characterise the microbiome and construct diagnostic model, and serum samples were detected using UPLC-MS to characterise lipid molecules. HCs, healthy controls; CPs, confirmed patients; SPs, suspected patients; CPRs, confirmed patients who recovered; RFC, random forest classifier; SPRs, suspected patients who recovered; UPLC-MS, ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.