Figure 2.
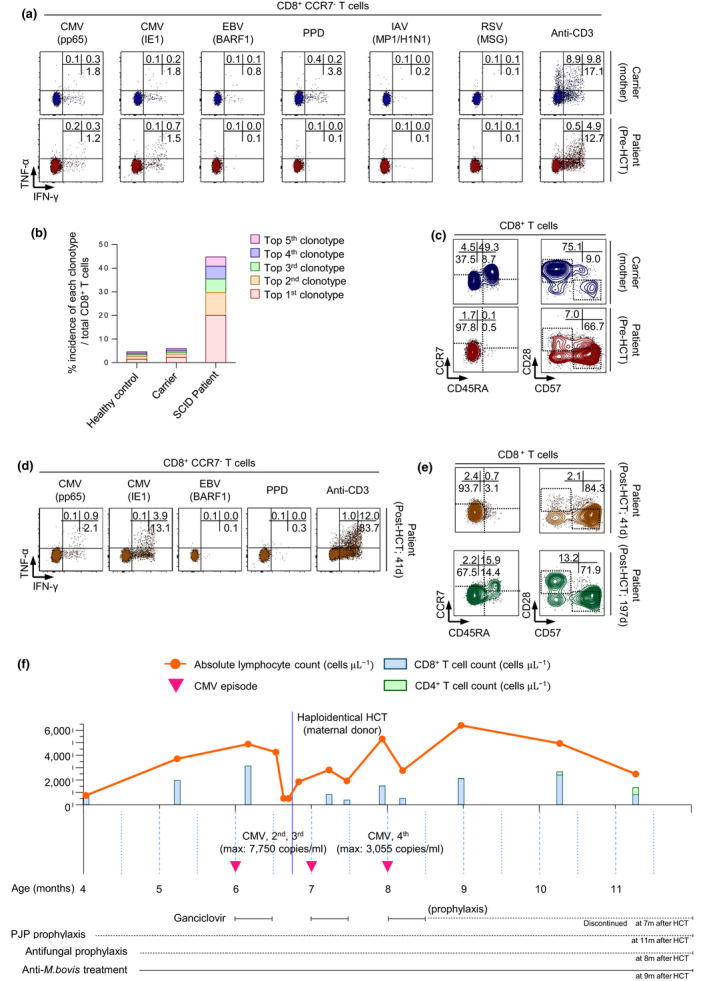
Maternal engrafted CD8+ T cells exert antiviral functions against CMV before and after HCT in the patient with SCID. (a) Maternal engrafted CD8+ T cells secreted TNF‐α and/or IFN‐γ in response to CMV antigen (pp65, IE1), but not to other antigens. (b) TCR repertoire analysis of CD8+ T cells from a healthy donor, mother (carrier) and the patient showed vigorous expansion of the oligoclonotypes of engrafted CD8+ T cells from the patient. (c) Immunophenotyping demonstrating an increased frequency of effector/effector memory (CD45RA−CCR7−) and replicative senescent (CD28−CD57+) CD8+ T cells from the patient. (d) Engrafted CD8+ T cells secreted higher levels of TNF‐α and/or IFN‐γ in response to CMV antigen after HCT than before HCT, and (e) exhibited a terminally differentiated immunophenotype, including effector/effector memory and replicative senescent populations. (f) Schematic of the time course of disease and treatments. The patient underwent haploidentical allogeneic HCT at the age of 6 months. Following HCT, there was no evidence of acute GVHD or disseminated infections, even with persistent CMV viraemia.
