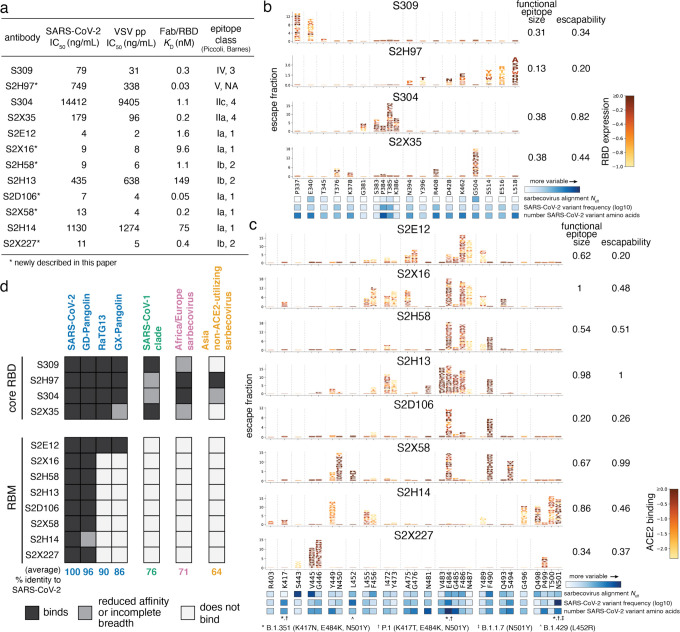
Fig. 1. Potency, escapability, and breadth in a diverse panel of RBD antibodies.
a, For a panel of 12 SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, summary of neutralization potency (authentic SARS-CoV-2-NLuc [n=3] and SARS-CoV-2 spike-pseudotyped VSV particles [n = 3 to 8] on Vero E6 cells, Extended Data Fig. 1a,b), 1:1 Fab:RBD binding affinities (SPR, Extended Data Fig. 1c), and epitope class according to the schemes of Piccoli et al.17 and Barnes et al.9 See Extended Data Table 1 for additional antibody details. Binding affinities for previously described antibodies measured in Piccoli et al. (S304, S2X35, S2H13, S2H14)17, Tortorici et al. (S2E12)8 and Cathcart et al. (S309)24 b,c, Complete maps of mutations that escape binding by antibodies targeting the core RBD (b) or receptor-binding motif [RBM] (c), as determined by a yeast-display deep mutational scanning method (Extended Data Fig. 2). In each map, the height of a letter indicates that mutation’s strength of escape from antibody binding. Letters are colored by their effects on folded RBD expression (b) or ACE2 binding affinity (c) [scale bars, right], as determined in our prior deep mutational scans28. See Extended Data Fig. 3 for escape maps colored by the opposite functional property. For each antibody, the relative “functional epitope size” and “escapability” are tabulated at right (see Methods for details). Heatmaps at bottom illustrate variability of each position within the sarbecovirus alignment or among globally sampled SARS-CoV-2 mutants. See Extended Data Fig. 4a for mutation-level variability and escape among observed SARS-CoV-2 mutants. Interactive escape maps and structural visualizations can be found at: https://jbloomlab.github.io/SARS-CoV-2-RBD_MAP_Vir_mAbs. d, Breadth of sarbecovirus binding by each antibody, summarizing comprehensive pan-sarbecovirus RBD yeast-display, ELISA, mammalian-display, and SPR binding assays. See Extended Data Fig. 5 for all data and phylogenetic definition of RBD clades. Black indicates an antibody binds an RBD or all RBDs within a clade with binding strength similar to SARS-CoV-2, gray indicates binding is reduced in affinity, or not all homologs within a clade are strongly bound, and white indicates no binding detected to a homolog or within a clade. The percent identity between RBD amino acid sequences with SARS-CoV-2 (or average % identity for clades) is shown below each column.